AP 10th Class Biology 5th Lesson Life Processes Important Questions
Class 10 Biology Chapter 5 Important Questions - 1 Mark
Question 1.
What is nutrition ?
Answer:
Nutrition is the process of taking in food and converting it into energy and other vital nutrients required for life.
Question 2.
What is autotrophic nutrition ?
Answer:
Autotrophic nutrition is a type of nutrition in which organisms produce their own food using sunlight or inorganic compounds, such as carbon dioxide and water. Plants, algae, and some bacteria exhibit autotrophic nutrition through the process of photosynthesis.
Question 3.
Define heterotrophic nutrition.
Answer:
Heterotrophic nutrition is a type of nutrition in which organisms obtain their food by consuming organic substances produced by other organisms. Animals, fungi, and some bacteria are examples of organisms that exhibit heterotrophic nutrition.
Question 4.
Name the pigment responsible for capturing sunlight in photosynthesis.
Answer:
Chlorophyll is the pigment responsible for capturing sunlight in photosynthesis.
Question 5.
What is the primary source of energy for organisms that undergo chemosynthesis?
Answer:
The primary source of energy for organisms that undergo chemosynthesis is chemical compounds, typically inorganic ones, rather than sunlight. Bacteria near hydrothermal vents are an example of organisms that use chemosynthesis.
Question 6.
Differentiate between saprophytic and parasitic nutrition.
Answer:
Saprophytic nutrition involves obtaining nutrients from dead organic matter, while parasitic nutrition involves obtaining nutrients from a living host organism, often causing harm to the host.
Question 7.
Name the process by which complex organic molecules are broken down into simpler ones with the release of energy.
Answer:
The process by which complex organic molecules are broken down into simpler ones with the release of energy is called catabolism.
Question 8.
Give an example of an organism that exhibits holozoic nutrition.
Answer:
An example of an organism that exhibits holozoic nutrition is a human. Holozoic nutrition involves the ingestion of solid organic food, digestion, and the absorption of nutrients.
Question 9.
What is the role of enzymes in nutrition ?
Answer:
Enzymes play a crucial role in nutrition by catalyzing chemical reactions involved in the breakdown of complex molecules into simpler forms that can be absorbed and utilized by the organism.
Question 10.
What is the primary function of the digestive system?
Answer:
The primary function of the digestive system is to break down food into nutrients that can be absorbed by the body for energy and other essential functions.
Question 11.
Where does the process of digestion begin?
Answer:
The process of digestion begins in the mouth.
Question 12.
Name the enzyme present in saliva that helps in the digestion of carbohydrates.
Answer:
The enzyme present in saliva that helps in the digestion of carbohydrates is amylase.
Question 13.
What is the role of the stomach in the digestive system?
Answer:
The stomach plays a crucial role in breaking down food mechanically and chemically. It secretes gastric juices that contain enzymes and acids to further digest food.
Question 14.
Where does the majority of nutrient absorption occur in the digestive system?
Answer:
The majority of nutrient absorption occurs in the small intestine.
Question 13.
What is the function of bile in digestion?
Answer:
Bile helps in the emulsification of fats, breaking them down into smaller particles to facilitate digestion and absorption.
Question 16.
Which organ produces insulin and glucagon, hormones important for digestion and metabolism ?
Answer:
The pancreas produces insulin and glucagon.
Question 17.
What is peristalsis in the context of the digestive system?
Answer:
Peristalsis is the rhythmic contraction and relaxation of muscles in the digestive tract, which helps move food along the digestive system.
Question 18.
Name the final part of the digestive system where water absorption takes place before the formation of feces.
Answer:
The colon (large intestine) is the final part of the digestive system where water absorption takes place before the formation of faeces.
Question 19.
Which organ stores bile and releases it as needed into the small intestine ?
Answer:
The gallbladder stores bile and releases it as needed into the small intestine.
Question 20.
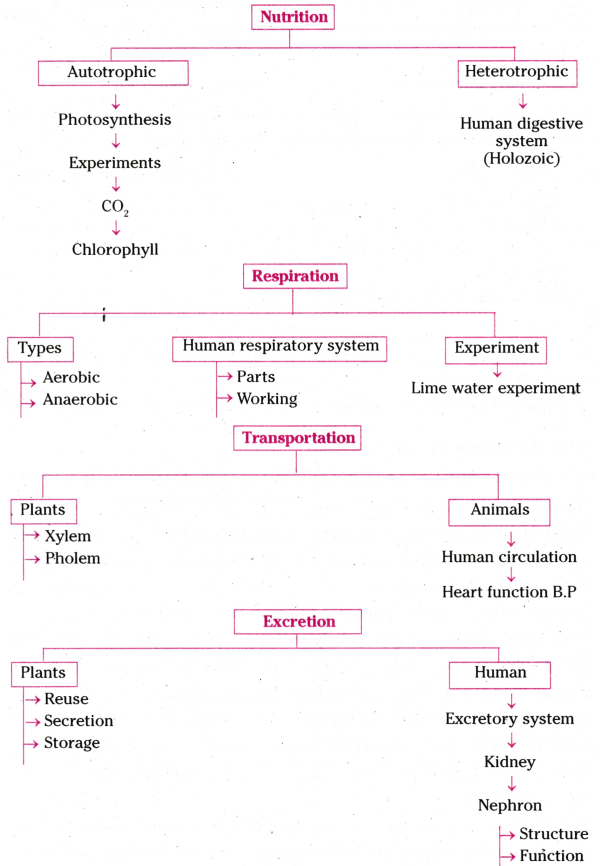
In the given diagram of a closed stomata (1), (2), (3) and (4) respectively are:
A) nucleus, chloroplast, guard cell, vacuole
B) nucleus, chloroplast, vacuole, guard cell
C) chloroplast, nucleus, vacuole, guard cell
D) vacuole, guard cell, nucleus, chloroplast
Answer:
B) nucleus, chloroplast, vacuole, guard cell
Question 21.
Assertion (A): Amoeba takes in food using finger like extensions of the cell surface. Reason (R) : In all unicellular organisms, the food is taken in by the entire cell surface.
A)Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
B) Both Assertion(A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
C) Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false.
D) Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true.
Answer:
A) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
Question 22.
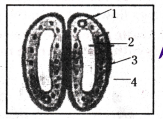
Opening and closing of stomata is due to
Answer:
Movement of water in and out of the guard cells.
Question 23.
Assertion (A): The inner walls of the small intestine have finger like projections called villi which are rich in blood.
Reason (R): These villi have a large surface area to help the small intestine in completing the digestion of food.
A) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
B) Both Assertion(A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
C) Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false.
D) Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true.
Answer:
C) Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false.
Question 24.
Which one of the following conditions is true for the state of stomata of a green leaf shown in the given diagram?
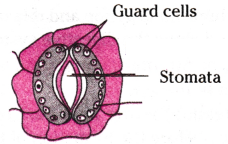
A) Large amount of water flows into the guard cells.
B) Gaseous exchange is occurring in large amount.
C) Large amount of water flows out from the guard cells.
D) Large amount of sugar collects in the guard cells.
Answer:
C) Large amount of water flows out from the guard cells.
Question 25.
A student was asked to write a stepwise procedure to demonstrate that carbon dioxide is necessary for photosynthesis. He wrote the following steps. The wrongly worded step is

A) Both potted plants are kept in dark room for at least three days.
B) Bottom of the bell jars is sealed to make them air tight.
C) Both potted plants are kept in sunlight after the starch test.
D) A leaf from both the plants is taken to test the presence of starch.
Answer:
C) Both potted plants are kept in sunlight after the starch test.
Question 26.
Given alongside is a sketch of a leaf partially covered with black paper and which is to be used in the experiment to show that light is compulsory for the process of photosynthesis. At the end of the experiment, which one of the leaf parks labelled I, II and III will become black when dipped in iodine solution ?
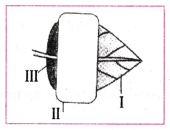
A) I only
B) II only
C) I and III
D) II and III
A.
C) I and III
Question 27.
Which region of the human digestive system releases bile juice?
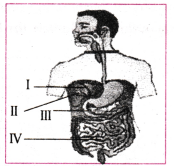
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
Answer:
A) I
Question 28.
Write the correct sequence for nutrition in Amoeba.
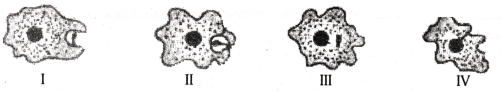
Answer:
IV, I, II, III
Question 29.
Which of the following diagram correctly shows pseudopodia in Amoeba?

Answer:
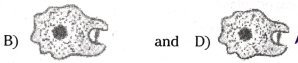
Question 30.
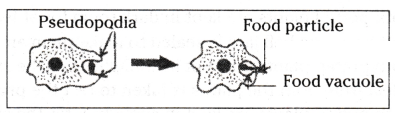
Which activity is illustrated in the diagram of an Amoeba shown above ?
Answer:
Ingestion
Question 31.
To set up an experiment to show that light is necessary for photosynthesis, leaves should be taken from
A) Destarched potted plant
B) Any potted plant
C) Any plant
D) Healthy plant
Answer:
A) Destarched potted plant
Question 32.
The function of KOH in the experimental set up to show that CO2 is released during respiration is to
A) Enhance respiration
B) Release oxygen for respiration
C) Absorb carbon dioxide released by germinating seeds
D) Remove water vapour from the flask
Answer:
C) Absorbcarbon dioxide released by germinating seeds
Question 33.
In the given transverse section of the leaf identify the layer of cells where maximum photosynthesis occurs
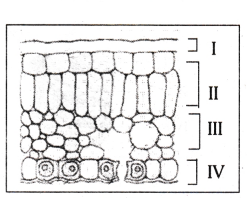
A) I, II
B) II, III
C) III, IV
D) I, IV
Answer:
B) II, III
Question 34.
Identify the option that indicates the correct enzyme that is secreted in location A, B and C.
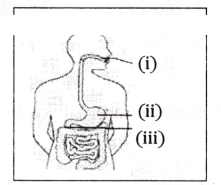
A) (i) - lipase, (ii) - trypsin, (iii) - pepsin
B) (i) - amylase, (ii) - pepsin, (iii) - trypsin
C) (i) - trypsin, (ii) - amylase, (iii) - carboxylase
D) (i) - permease, (ii) - carboxylase, (iii) - oxidase
Answer:
B) (i) - amylase, (ii) - pepsin, (iii) - trypsin
Question 35.
Observe the diagram of Human digestive system.
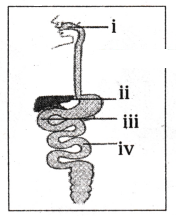
Match the labeling referred in column I and correlate with the function in column II.
| Column I |
Column II |
| i |
a) The length of this depends on food the organism eats. |
| ii |
b) Initial phase of starch digestion |
| iii |
c) Increase the efficiency of lipase enzyme action |
| iv |
d) This is the site of the complete digestion of carbohydrates, proteins and fats. |
A) i - a; ii - b; iii - c; iv - d
B) i - b ; ii - c; iii - d ; iv - a
C) i - b; ii - d; iii - c; iv - a
D) i - d; ii - a; iii - b; iv - c
A.
B) i - b ; ii - c; iii - d ; iv - a
Question 36.
Identify the option that indicates the correct enzyme that is secreted in location L, M and N. L, M and N represent Mouth cavity, stomach and small intestine of the human being.
|
L |
M |
N |
| A |
lipase |
tyrpsin |
pepsin |
| B |
amylase |
pepsin |
trypsin |
| C |
trypsin |
amylase |
lipase |
| D |
lipase |
amylase |
pepsin |
Answer:
B) L-amylase; M-pepsin; N - trypsin
Question 37.
Which metabolism is explained in this equation?

Answer:
Photosynthesis.
Question 38.
What is the use of these structures?
Answer:
Gases exchange and transpiration.
Question 39.
What is the diagram in this figure?
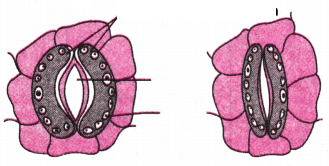
Answer:
Stomata opening and closing.
Question 40.
What is the type of nutrition in this figure?
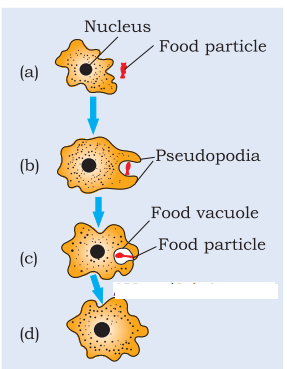
Answer:
Holozoic nutrition in amoeba.
Question 41.
What is the primary function of the respiratory system ?
Answer:
The primary function of the respiratory system is to facilitate the exchange of gases, specifically oxygen and carbon dioxide, between the body and the external environment.
Question 42.
Name the organs involved in the human respiratory system.
Answer:
The organs involved in the human respiratory system are the nose, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, bronchioles, and lungs.
Question 43.
What is the role of mucus in the respiratory system?
Answer:
Mucus in the respiratory system helps to trap and remove dust, bacteria, and other particles, preventing them from entering the lungs. It also adds moisture to the air we breathe.
Question 44.
Define the term "alveoli."
Answer:
Alveoli are tiny air sacs within the lungs where the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide takes place between the air and the bloodstream.
Question 45.
What is the process by which oxygen is transported from the lungs to the body tissues ?
Answer:
Oxygen is transported from the lungs to the body tissues through the bloodstream, primarily by binding to hemoglobin in red blood cells.
Question 46.
Explain the significance of the diaphragm in breathing.
Answer:
The diaphragm is a muscular partition separating the chest and abdominal cavities. It plays a crucial role in breathing by contracting and relaxing, causing changes in thoracic volume and creating the pressure differences needed for inhalation and exhalation.
Question 47.
Name the respiratory control center in the brain.
Answer:
The respiratory control center in the brain is located in the medulla oblongata.
Question 48.
What is the term for the process of breathing out air from the lungs?
Answer:
The process of breathing out air from the lungs is called exhalation or expiration.
Question 49.
How does smoking affect the respiratory system ?
Answer:
Smoking can damage the respiratory system by causing irritation, inflammation, and reduced function of the airways. It also increases the risk of respiratory infections and diseases like chronic bronchitis and lung cancer.
Question 50.
What is the purpose of cilia in the respiratory tract ?
Answer:
Cilia are tiny hair-like structures that line the respiratory tract and help to move mucus and trapped particles upward towards the throat, where they can be swallowed or expelled. This helps in keeping the airways clear.
Question 51.
What is energy currency ?
Answer:
ATP is the energy currency for most cellular processes.
Question 52.
What is the primary purpose of cellular respiration in humans ?
Answer:
The primary purpose of cellular respiration in humans is to generate ATP (adenosine triphosphate), the cell’s main energy currency, by breaking down glucose and other organic molecules.
Question 53.
Which organelle is responsible for cellular respiration in eukaryotic cells ?
Answer:
Mitochondria are responsible for cellular respiration in eukaryotic cells.
Question 54.
What is the starting molecule for glycolysis?
Answer:
Glucose is the starting molecule for glycolysis.
Question 55.
In which cellular compartment does the Krebs cycle (citric acid cycle) take place ?
Answer:
The Krebs cycle takes place in the mitochondrial matrix.
Question 56.
What is the final electron acceptor in the electron transport chain during cellular respiration ?
Answer:
Oxygen is the final electron acceptor in the electron transport chain.
Question 57.
What is the net gain of ATP molecules produced during glycolysis ?
Answer:
The net gain of ATP molecules produced during glycolysis is 2 ATP molecules.
Question 58.
Name the two main stages of cellular respiration.
Answer:
The two main stages of cellular respiration are glycolysis and oxidative phosphorylation (which includes the Krebs cycle and the electron transport chain).
Question 59.
What is the role of NADH and FADH2 in cellular respiration ?
Answer:
NADH and FADH2 serve as electron carriers, donating electrons to the electron transport chain to generate a proton gradient and ultimately produce ATP.
Question 60.
Define aerobic respiration.
Answer:
Aerobic respiration is the process of cellular respiration that occurs in the presence of oxygen, leading to the complete oxidation of glucose and the production of ATP.
Question 61.
What is the end product of glycolysis ?
Answer:
The end products of glycolysis are two molecules of pyruvate, along with ATP and NADH.
Question 62.
In living organisms during respiration which of the following products are not formed if oxygen is not available ?
A) Carbon dioxide + Water
B) Carbon dioxide + Alcohol
C) Lactic acid + Alcohol
D) Carbon dioxide + Lactic Acid
Answer:
A) Carbon dioxide + Water
Question 63.
Which of the following statements are correct in reference to the role of A (shown in the given diagram) during a breathing cycle In human beings ?
i) It helps to decrease the residual volume of air in lungs.
ii) It flattens as we inhale.
iii) It gets raised as we inhale.
iv) It helps the chest cavity to become larger.
A) (ii) and (iv)
B) (iii) and (iv)
C) (i) and (ii)
D) (i), (ii) and (iv)
Answer:
A) (ii) and (iv)
Question 64.
Respiratory structures of two different animals a fish and a human being are as shown.
Observe (a) and (b) and select one characteristic that holds true for both of them.
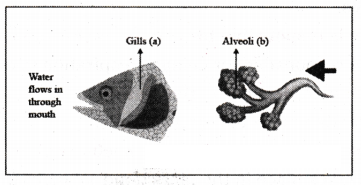
A) Both are placed internally in the body of animal.
B) Both have thin and moist surface for gaseous exchange.
C) Both are poorly supplied with blood vessels to conserve energy.
D) In both the blood returns to the heart after being oxygenated.
Answer:
B) Both have thin and moist surface for gaseous exchange.
Question 65.
A sportsman, after a long break of his routine exercise, suffered muscular cramps during a heavy exercise session. Why this happened ?
Answer:
Lack of oxygen and formation of lactic acid.
Question 66.
Observe the experimental setup shown below. Name the chemical indicated as ‘X’ that can absorb the gas which is evolved as a by product of respiration.
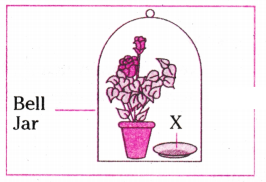
Answer:
KOH
Question 67.
Carefully study the diagram of the human respiratory system with labels A, B, C and D. Which gives correct identification and main function and/or characteristic?
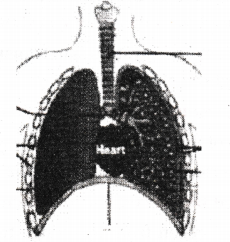
A) i) Trachea : It is supported by bony rings for conducting inspired air.
B) ii) Ribs : When we breathe out, ribs are lifted
C) iii) Alveoli: Thin-walled sac like structures for exchange of gases
D) iv) Diaphragm : It is pulled up when we breathe in
Answer:
C) iii) Alveoli: Thin-walled sac like structures for exchange of gases
Question 68.
What is a catabolic process ? Give an example.
Answer:
It is the process in which bigger molecules are broken into smaller molecules. Respiration is the catabolic process.
Question 69.
What are the structures shown in the diagram with arrow mark ?
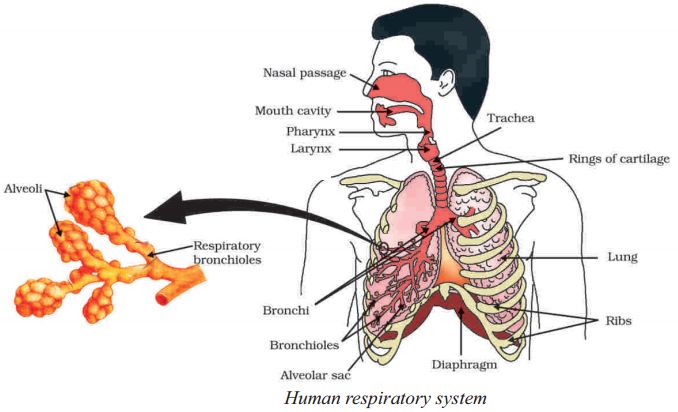
Answer:
Alveoli.
Question 70.
Does yoga Improve the respiratory system?
Answer:
Both Asanas and yoga breathing exercises maintain the health of your respiratory system overall.
Question 71.
What is the importance of exercise?
Answer:
Being physically active can improve your brain health, help manage weight, reduce the risk of disease, strengthen bones and muscles and improve your ability to do everyday activities.
Question 72.
What is the effect of smoking?
Answer:
- Smoking is injurious to health.
- Lung cancer is one of common causes of smoking.
Question 73.
What is the main function of the circulatory system ?
Answer:
The main function of the circulatory system is to transport oxygen, nutrients, hormones, and waste products throughout the body.
Question 74.
Name the four main components of the human circulatory system.
Answer:
The four main components of the human circulatory system are the heart, blood vessels (arteries, veins, and capillaries), blood, and lymphatic system.
Question 75.
What is the function of red blood cells in the circulatory system ?
Answer:
Red blood cells transport oxygen from the lungs to the rest of the body and carry carbon dioxide, a waste product, back to the lungs for exhalation.
Question 76.
What is the role of arteries in the circulatory system ?
Answer:
Arteries carry oxygenated blood away from the heart to various parts of the body.
Question 77.
Define the term "blood pressure."
Answer:
Blood pressure is the force exerted by the blood against the walls of the blood vessels, especially the arteries, and is measured in millimeters of mercury (mmHg).
Question 78.
Which chamber of the heart pumps oxygenated blood to the rest of the body?
Answer:
The left ventricle pumps oxygenated blood to the rest of the body.
Question 79.
What is the purpose of valves in the heart?
Answer:
Valves in the heart prevent the backflow of blood, ensuring that blood flows in one direction through the heart chambers.
Question 80.
Name the largest artery in the human body.
Answer:
The largest artery in the human body is the aorta.
Question 81.
What is the function of white blood cells in the circulatory system?
Answer:
White blood cells play a crucial role in the immune system, defending the body against infections and foreign invaders.
Question 82.
What is the difference between veins and arteries in terms of blood flow?
Answer:
Arteries carry blood away from the heart, while veins carry blood toward the heart.
Question 83.
What is the primary function of xylem in plants ?
Answer:
The primary function of xylem in plants is to transport water and minerals from the roots to the other parts of the plant.
Question 84.
Name the process by which water moves from the roots to the leaves in plants.
Answer:
The process by which water moves from the roots to the leaves in plants is called transpiration.
Question 85.
What is the role of phloem in plants ?
Answer:
Phloem in plants is responsible for the transport of sugars (mainly sucrose) produced during photosynthesis from the leaves to other parts of the plant.
Question 86.
Define the term "transpiration."
Answer:
Transpiration is the process by which water is absorbed by plant roots, travels through the plant, and is released into the atmosphere as water vapour through small pores called stomata in the leaves.
Question 87.
Which vascular tissue is responsible for the upward movement of water in plants?
Answer:
Xylem is responsible for the upward movement of water in plants.
Question 88.
Name the tiny openings on the surface of leaves through which water vapor is released.
Answer:
The tiny openings on the surface of leaves through which water vapour is released are called stomat
Answer:
Question 89.
How lymph is formed ?
Answer:
Through the pores present in the walls of capillaries some amount of plasma, proteins and blood cells escape into intercellular spaces in the tissues to form the tissue fluid or lymph.
Question 90.
In which direction does the movement of phloem sap occur in plants ?
Answer:
The movement of phloem sap in plants occurs bidirectionally, both upward -towards the leaves, and downward -towards the roots.
Question 91.
What is the driving force behind the movement of water in the xylem ?
Answer:
Transpiration pull, created by the evaporation of water from the leaves, is the driving force behind the movement of water in the xylem.
Question 92.
Name the two types of cells found in xylem tissue.
Answer:
The two types of cells found in xylem tissue are tracheids and vessel elements.
Question 93.
Observe the following diagram and write the name of the process and its significance.
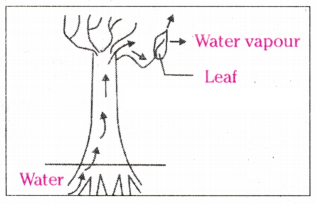
Answer:
Transpiration: creates a suction force which pulls water inside the plant.
Question 94.
Consider the following statements in connection with the functions of the blood vessels marked A and B in the diagram of a human heart as shown.
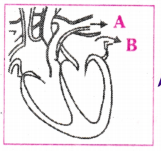
ii) Blood vessel B - It carries oxygen rich blood from the lungs.
iii) Blood vessel B - Left atrium relaxes as it receives blood from this blood vessel.
iv) Blood vessel A - Right atrium has thick muscular wall as it has to pump blood to this blood vessel.
Write the correct statements.
Answer:
(i), (ii) and (iii) are correct statements.
Question 95.
Assertion (A): Nitrogen is an essential element for plant growth and is taken up by plants in the farm of inorganic nitrates or nitrites.
Reason (R) : The soil is the nearest and richest source of raw materials like Nitrogen, Phosphorus and other minerals for the plants.
Choose the correct answer :
A) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
B) Both Assertion(A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
C) Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false.
D) Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true.
Answer:
B) Both Assertion(A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
Question 96.
Identify the two components of Phloem tissue that help in transportation of food in plants.
A) phloem parenchyma & sieve tubes
B) sieve tubes & companion cells
C) phloem parenchyma & companion cells
D) phloem fibres and sieve tubes A.
Answer:
B) sieve tubes & companion cells
Question 97.
Assertion (A) : Amphibians can tolerate mixing of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood.
Reason (R) : Amphibians are animals with two chambered heart.
Choose the correct answer.
A) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
B) Both A and R are true and R is not the correct explanation of A
C) A is true but R is false
D) A is False but R is true
Answer:
C) A is true but R is false
Question 98.
The figure given below shows a schematic plan of blood circulation in humans with labels (i) to (iv). Identify the correct label with its functions ?
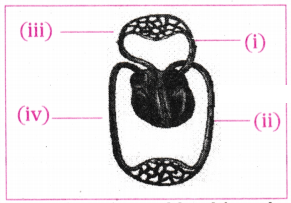
A) i) Pulmonary vein - takes impure blood from body part.
B) ii) Pulmonary artery - takes blood from lung to heart.
C) iii) Aorta - takes blood from heart to body parts.
D) iv) Vena cava takes - blood from body parts to right auricle.
Answer:
D) iv) Vena cava takes - blood from body parts to right auricle.
Question 99.
Write the phase of circulation which is represented in the diagram of heart given below. Arrows indicate contraction of the chambers shown.
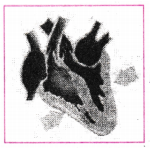
Answer:
Blood is transferred to lungs for oxygenation and is pumped into various organs simultaneously.
Question 100.
In which of the following groups of organisms, blood flows through the heart only once during one cycle of passage through the body ?
A) Rabbit, Parrot, Turtle
B) Frog, Crocodile, Pigeon
C) Whale, Labeo, Penguin
D) Shark, Dog fish, Sting ray
Answer:
D) Shark, Dog fish, Sting ray
Question 101.
Given below are the functions of some parts of human circulatory system. Identify the correct match.
A) Pulmonary vein - takes oxygenated blood from body parts to heart
B) Artery - takes oxygenated blood from heart to lung
C) Dorsal aorta - takes deoxygenated blood from heart to body parts
D) Vena cava - takes deoxygenated blood from body parts to right atrium
Answer:
D) Vena cava - takes deoxygenated blood from body parts to right atrium
Question 102.
Assertion : The muscular walls of ventricles are thicker than auricles.
Reason : This helps in preventing the back flow of blood. Given explanation. Give explanation.
Answer:
Explanation : Since ventricles have to pump blood into various organs, they have thicker muscular wall than atria valves prevent back flow of blood.
Question 103.
What is the use of this apparatus ?

Answer:
It’s the sphygmomanometer, used for to measure blood pressure.
Question 104.
What are the arrow marks indicated in this diagram ?
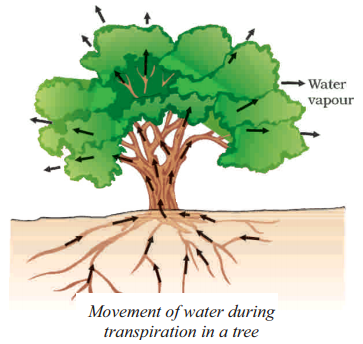
Answer:
Water transport.
Question 105.
What is the healthy B.P. value ?
Answer:
120/80 mmHg.
Question 106.
What is the primary organ responsible for the excretion of waste in humans?
Answer:
The primary organ responsible for the excretion of waste in humans is the kidney.
Question 107.
Name the functional unit of the kidney involved in filtration.
Answer:
The functional unit of the kidney involved in filtration is the nephron.
Question 108.
What is the main nitrogenous waste product excreted by humans?
Answer:
The main nitrogenous waste product excreted by humans is urea.
Question 109.
Which process involves the removal of excess water and solutes from the blood, forming urine ?
Answer:
The process that involves the removal of excess water and solutes from the blood, forming urine, is filtration.
Question 110.
What is the role of the urethra in the excretory system ?
Answer:
The urethra serves as the tube through which urine is expelled from the body during the process of micturition (urination).
Question 111.
Name the hormone that regulates the reabsorption of water in the kidney tubules.
Answer:
The hormone that regulates the reabsorption of water in the kidney tubules is antidiuretic hormone (ADH).
Question 112.
Which blood vessel brings blood to the kidney for filtration ?
Answer:
The renal artery brings blood to the kidney for filtration.
Question 113.
What is the term for the process of expelling urine from the bladder ?
Answer:
The process of expelling urine from the bladder is called micturition or urination.
Question 114.
What is the significance of the loop of Henle in the kidney ?
Answer:
The loop of Henle plays a crucial role in the concentration of urine by facilitating the reabsorption of water and ions.
Question 115.
Name one function of the urinary bladder.
Answer:
One function of the urinary bladder is to temporarily store urine until it is ready to be expelled from the body.
Question 116.
What is excretion ?
Answer:
The biological process involved in the removal of these harmful metabolic wastes from the body is called excretion.
Question 117.
How do unicellular organisms remove their waste products ?
Answer:
Many unicellular organisms remove these wastes by simple diffusion from the body surface into the surrounding water.
Question 118.
What is the primary excretory product in plants ?
Answer:
The primary excretory product in plants is oxygen.
Question 119.
Name the process through which plants eliminate excess water in the form of water vapor.
Answer:
Transpiration.
Question 120.
Which cellular organelle is responsible for the storage of waste products in plant cells ?
Answer:
Vacuole.
Question 121.
What is the role of stomata in the process of excretion in plants ?
Answer:
Stomata allow the release of oxygen produced during photosynthesis and the removal of excess water vapor through transpiration.
Question 122.
How do plants excrete metabolic wastes produced during cellular activities ?
Answer:
Metabolic wastes in plants are often stored in vacuoles or eliminated through shedding of leaves.
Question 123.
What if the dog or the cow or the man were asleep? We would still think that they were alive, but how did we know that?
Answer:
We see them breathing, and we know that they are alive.
Question 124.
Is this invisible molecular movement necessary for life ?
Answer:
Yes. Infact all life processes have invisible molecular movements.
Question 125.
What are life processes ?
Answer:
To maintain life, organisms have to perform certain functions such as nutrition, respiration, reproduction and excretion etc., which are called life processes.
Question 126.
Which one among the following is not removed as a waste product from the body of a plant ?
A) Resins and Gums
B) Urea
C) Dry Leaves
D) Excess Water
Answer:
B) Urea
Question 127.
Assertion (A) : Resins and gums are stored in old xylem tissue in plants.
Reason (R) : Resins and gums facilitate transport of water molecules.
Choose the correct answer.
A) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
B) Both A and R are true and R is not the correct explanation of A
C) A is true but R is false
D) A is False but R is true
A.
C) A is true but R is false
Question 128.
What is common between extensive network of blood vessels around walls of alveoli and in glomerulus of nephron ?
Answer:
Thin walled capillaries richly supplied with blood.
Question 129.
Plants use completely different porcess for excretion as compared to animals. Which one of the following processes is NOT followed by plants for excretion ?
A) They can get rid of excess water by transpiration.
B) They selectively filter toxic substances through their leaves.
C) Waste products are stored as resins and gums in old xylem.
D) They excrete waste substances into the soil around them.
Answer:
B) They selectively filter toxic substances through their leaves.
Question 130.
What is the unit shown in the diagram?
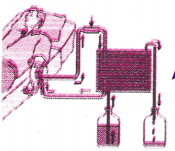
Answer:
Dialysis unit.
Question 131.
Why do we take plenty of water?
Answer:
Drinking water can prevent dehydration, a condition that can cause unclear thinking, result in mood change, cause your body to overheat, and lead to constipation and kidney stones.
Question 132.
Why is Hemodialysis needed ?
Answer:
Failure of both kidney needs to Hemodialysis.
Life Processes Class 10 Important Questions - 2 Marks
Question 1.
How the unicellular organisms maintain their life process?
Answer:
In the case of a single-celled organism, no specific organs for taking in food, exchange of gasses or removal of wastes may be needed because the entire surface of the organism is in contact with the environment.
Question 2.
Why is the diffusion process not enougli in multicellular organisms ?
Answer:
In multicellular organisms, all the cells may not be in direct contact with the surrounding environment. Thus, simple diffusion will not meet the requirements of all the cells.
Question 3.
What is the need of the transport system ?
Answer:
The food and oxygen are now taken up at one place in the body of the organisms, while all parts of the body need them. This situation creates a need for a transportation system for carrying food and oxygen from one place to another in the body.
Question 4.
What is the need of the excretory system ?
Answer:
When chemical reactions use the carbon source and the oxygen for energy generation, they create by-products that are not only useless for the cells of the body, but could even be harmful. These waste byproducts are therefore needed to be removed from the body and discarded outside by a process called excretion.
Question 5.
Why do we need food ?
Answer:
Energy is needed to maintain a state of order in our body. We also need materials from outside in order to grow, develop, synthesize protein and other substances needed in the body. This source of energy and materials is the food we eat.
Question 6.
What are autotrophs ?
Answer:
Some organisms use simple food material obtained from inorganic sources in the form of carbon dioxide and water. These organisms are called the autotrophs, include green plants and some bacteria.
Question 7.
What are heterotrophs ?
Answer:
Some organisms utilize complex substances or the body energy. These complex substances have to be broken down into simpler ones before they can be used for the upkeep and growth of the body. To achieve this, organisms use bio-catalysts called enzymes. These are called heterotrophs. The heterotroph’s survival depends directly of indirectly on autotrophs. Heterotrophic organisms include animals and fungi.
Question 8.
Define photosynthesis.
Answer:
- Photosynthesis is the process that plants use to convert light energy into sugar molecules.
- The equation for photosynthesis is :
carbon dioxide + water + sunlight → oxygen and glucose.
6CO2 + 6H2O + sunlight → C6H12O6 + 6O2
Question 9.
What actually happens during the process of photosynthesis?
Answer:
The following events occur during this process :
- Absorption of light energy by chlorophyll.
- Conversion of light energy to chemical energy and splitting of water molecules into hydrogen and oxygen.
- Reduction of carbon dioxide to carbohydrates.
Question 10.
How desert plants differ in photosynthesis ?
Answer:
Desert plants take up carbon dioxide at night and prepare an intermediate which is acted upon by the energy absorbed by the chlorophyll during the day.
Question 11.
What is chlorophyll ? Where is it located ?
Answer:
We find green dots in the section of leaf. These green dots are cell organelles called chloroplasts which contain chlorophyll, that chlorophyll is essential for photosynthesis.
Question 12.
What is heterotrophic nutrition ?
Answer:
Heterotrophic nutrition is a mode of nutrition in which organisms depend upon other organisms for food to survive. They can’t make their own food like Green plants. Heterotrophic organisms have to take in all the organic substances they need to survive.
Question 13.
What are the different types of heterotrophic nutrition?
Answer:
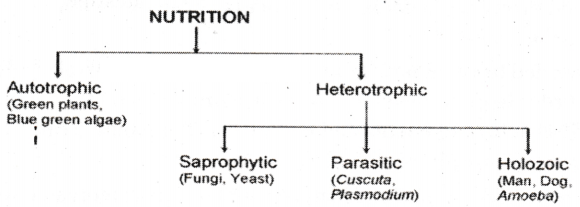
Heterotrophic nutrition can be one of three types - holozoic, saprophytic or parasitic. Holozoic nutrition can be seen in most vertebrates and some unicellular organisms like the amoeba.
Question 14.
What is saprophytic nutrition ?
Answer:
Some organisms break-down the food material outside the body and then absorb it. This type of neutron is saprophytic nutrition. Examples are fungi like bread moulds, yeast and mushrooms.
Question 15.
What is holozoic nutrition ?
Answer:
Holozoic Nutrition is when an organism consumes a variety of organic material, which then undergoes a series of metabolic processes such as digestion, absorption, and assimilation. Amoebae, which are organisms with only one cell, are known to rely on this kind of holozoic for survival.
Question 16.
What is parasitic nutrition ?
Answer:
Parasitic Nutrition is a mode of heterotrophic nutrition where an organism lives on the body surface or inside the body of another type of organism known as a parasite, where the parasite lives as a host. The parasite obtains nutrition directly from the body of the hosts, like cuscuta (amarbel), ticks, lice, leeches and tape-worms.
Question 17.
When we eat something we like, our mouth ‘waters’. What is it?
Answer:
This is actually not only water, but a fluid called saliva secreted by the salivary glands, which help in digestion and make the food lubricant and make a food boul called bolus.
Question 18.
What is the role of enzymes in the digestive system?
Answer:
The food we ingest is of a complex nature. If it is to be absorbed from the alimentary canal, it has to be broken into smaller molecules. This is done with the help of biological catalysts called enzymes.
Question 19.
How the saliva helps in design?
Answer:
- The saliva contains an enzyme called salivary amylase that breaks down starch which is a complex molecule to give simple sugar.
- The food is mixed thoroughly with saliva and moved around the mouth while chewing by the muscular tongue.
Question 20.
How the food moved in the digestive tract ?
Answer:
- It is necessary to move the food in a regulated manner along the digestive tube, so that it can be processed properly in each part.
- The lining of the canal has muscles that contract rhythmically in order to push the food forward. These peristaltic movements occur all along the gut.
Question 21.
What are the parts in the human digestive system?
Answer:
- Mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, and anus are the major parts in digestive tract.
- The liver, pancreas, and gallbladder are the glands of the digestive system.
Question 22.
Why small intestine is coiled ?
Answer:
From the stomach, the food now enters the small intestine. This is the longest part of the alimentary to complete the digestion, which is fitted into a compact space because of extensive coiling.
Question 23.
Why herbivores have a long intestine ?
Answer:
The length of the small intestine differs in various animals depending on the food they eat. Herbivores eating grass need a longer small intestine to allow the cellulose to be digested. Meat is easier to digest, hence carnivores like tigers have a shorter small intestine.
Question 24.
What are villi? What is its role?
Answer:
- Digested food is taken up by the walls of the intestine. The inner lining of the small intestine has numerous finger-like projections called villi which increase the surface area for absorption.
- The villi are richly supplied with blood vessels which take the absorbed food to each and every cell of the body.
Question 25.
How the waste material is removed from our body ?
Answer:
The unabsorbed food is sent into the large intestine where its wall absorbs more water from this material. The rest of the material is removed from the body via the anus. The exit of this waste material is regulated by the anal sphincter.
Question 26.
What is autotrophic nutrition?
Answer:
Autotrophic nutrition is a type of nutrition in which organisms produce their own food using sunlight or inorganic compounds. Plants are examples of organisms that exhibit autotrophic nutrition through photosynthesis.
Question 27.
Define heterotrophic nutrition.
Answer:
Heterotrophic nutrition is a type of nutrition in which organisms obtain their food by consuming other organic substances. Animals, fungi, and many bacteria are examples of organisms that rely on heterotrophic nutrition.
Question 28.
Explain the process of photosynthesis.
Answer:
Photosynthesis is the process by which green plants, algae, and some bacteria, convert light energy into chemical energy in the form of glucose. It involves the absorption of sunlight, carbon dioxide from the air, and water from the soil to produce glucose and oxygen. The equation for photosynthesis is
6CO2+ 6H2O + light energy → C6H12O6 + 6O2
Question 29.
Differentiate between saprophytic and parasitic nutrition.
Answer:
Saprophytic nutrition is a type of nutrition in which organisms obtain nutrients from dead or decaying organic matter. In contrast, parasitic nutrition is a type of nutrition in which organisms derive nutrients from a living host organism, often causing harm to the host.
Question 30.
Give an example of a symbiotic relationship involving nutrition.
Answer:
An example of a symbiotic relationship involving nutrition is the relationship between nitrogen-fixing bacteria and leguminous plants. The bacteria fix atmospheric nitrogen into a form that the plant can use, and, in return, the plant provides the bacteria with carbohydrates.
Question 31.
What is the role of enzymes in digestion?
Answer:
Enzymes play a crucial role in digestion by catalyzing the breakdown of complex food molecules into simpler forms that can be absorbed by the body. For example, amylase breaks down carbohydrates, protease breaks down proteins, and lipase breaks down fats.
Question 32.
Define omnivorous nutrition.
Answer:
Omnivorous nutrition is a type of nutrition in which organisms consume both plant and animal matter. Humans are examples of omnivores as they eat a variety of foods, including fruits, vegetables, meat, and dairy products.
Question 33.
What do we actually mean when we say that the "enzymes are specific in their action" ?
Answer:
- Enzymes are the proteins that speed up the breaking of complex substances to simpler substances.
- Enzymes active site have specific shape and hence bind with specific substrate thereby catalysing only specific reaction.
Question 34.
Explain why photosynthesis is considered the most important process in the biosphere.
Answer:
Photosynthesis is considered the most important process in biosphere due to following reasons:
- It is the primary source of food on earth.
- It is also responsible for the release of oxygen into the atmosphere by green plants which is needed by mostly all life forms.
Question 35.
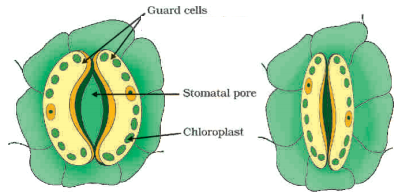
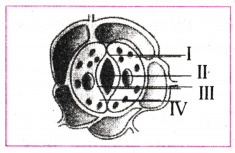
In the following sketch of stomatal apparatus, parts I, II, III and IV were labelled differently by four students. Name the labelling I, II, III and IV.
Answer:
(I) cytoplasm, (II) nucleus, (III) stoma, (IV) chloroplast.
Question 36.
Bile juice does not have any digestive enzyme but still plays a significant role in the process of digestion. Justify the statement.
Answer:
Bile juice is secreted by liver. Bile salts break the large globules of fat in the intestine to smaller globules increasing the efficiency of enzyme action. It makes the acidic food from the stomach alkaline for the action of pancreatic enzymes. This is similar to the emulsifying action of soaps on dirt.
Question 37.
Life depends on Sun - Give Reason.
Answer:
All living things constantly need energy to live. They get energy in the form of food. The food directly or indirectly comes from the green plants. The green plants trap solar energy comes from the sun to produce food during photosynthesis.
Question 38.
Rajiv ate chapathi it did not digest in the stomach - Give Reason.
Answer:
In the stomach Gastric juice secretes pepsin, it digest only proteins to Amino acids chapathi is the carbohydrate - salivary. Amylase can act on carbohydrate to digest to form glucose. So, chapathi did not digest in stomach.
Question 39.
Read the paragraph and answer the following questions.
The unabsorbed food is sent into the large intestine where its wall absorbs more water from this material. The rest of the material is removed from the body via the anus. The exit of this waste material is regulated by the anal sphincter.
1. Name the organ that is described in this paragraph ?
Answer: Large intestine.
2. What is the end part of the digestive system ?
Answer: Anus.
Question 40.
What is respiration?
Answer:
Respiration is the process in which the cells of an organism obtain energy by combining oxygen and glucose, resulting in the release of carbon dioxide, water, and ATP (energy).
C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O + ATP
Question 41.
What are the types in respiration?
Answer:
There are two types of Respiration: Aerobic Respiration - Takes place in the presence of oxygen. Anaerobic Respiration -Takes place in the absence of oxygen.
Question 42.
How smoking affects your health ?
Answer:
Smoking is injurious to health. Lung cancer is one of the common causes of deaths in the world. The upper part of the respiratory tract is provided with small hair-like structures called cilia. These cilia help to remove germs, dust and other harmful particles from inhaled air. Smoking destroys these hairs due to which germs, dust, smoke and other harmful chemicals enter lungs and cause infection, cough and even lung cancer.
Question 43.
Describe the process of inhalation during the respiratory cycle.
Answer:
Inhalation is the process of breathing in air. It involves the contraction of the diaphragm and the external intercostal muscles. The diaphragm moves downward, and the ribcage expands, increasing the thoracic volume. This decrease in pressure within the thoracic cavity allows air to rush into the lungs, filling the alveoli with oxygen.
Question 44.
Explain the role of the alveoli in the respiratory system.
Answer:
Alveoli are small air sacs located at the end of bronchioles in the lungs. They are the primary site for gas exchange in the respiratory system. Oxygen from the inhaled air diffuses across the thin walls of the alveoli into the bloodstream, while carbon dioxide, a waste product, diffuses from the blood into the alveoli to be exhaled. This exchange of gases is crucial for maintaining proper oxygen levels in the body and eliminating carbon dioxide.
Question 45.
Differentiate between inspiration and expiration.
Answer:
Inspiration is the process of inhaling or breathing in air. It involves the contraction of the diaphragm and external intercostal muscles, expanding the thoracic cavity and creating a pressure gradient that allows air to enter the lungs. On the other hand, expiration is the process of exhaling or breathing out air. It typically involves the relaxation of the diaphragm and external intercostal muscles, causing the thoracic cavity to decrease in volume and expel air from the lungs.
Question 46.
In the experimental set up to show that "CO2 is given out during respiration", name the substance taken in the small test tube kept in the conical flask. State its function and the consequence of its use.
Answer:
- Potassium hydroxide (KOH) is the substance taken in the small test tube.
- It absorbs carbon dioxide released by the seeds and a partial vacuum is created in the flask. This causes the water level in the delivery tube to rise.
Question 47.
What is anaerobic respiration ?
Answer:
The process of break down of glucose in the absence of oxygen is called an aerobic respiration. In this process, small amount of energy is released.
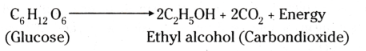
Question 48.
When a sports man runs, he often gets muscle cramps. Why ?
Answer:
- In order to release more energy to perform sudden activity, pyruvate is converted into lactic acid due to lack of oxygen.
- Formation of lactic acid in the muscles cause cramps or fatigue.
Question 49.
Stomata of desert plants remain closed during day time. How do they take up CO2 and perform photosynthesis?
Answer:
- The desert plants are scoto active. Their stomata open during night.
- Therefore they take up CO2 at night and produce intermediate inorganic acid which breakes up to release CO2.
- The CO2 produced internally is used in photosynthesis during day when stomata are closed.
Question 50.
Why is there a difference in the rate of breathing between aquatic organisms and terrestrial organisms ? Explain.
Answer:
- Terrestrial organisms can obtain oxygen directly from the air and have slow breathing rate, but aquatic organisms have to obtain oxygen for respiration which is dissolved in water.
- Since the amount of oxygen dissolved in water is fairly low as compared to the amount of oxygen in air, the rate of breathing in aquatic organisms is much faster.
Question 51.
Give reason for the diffusion does not take place in large body size animals.
Answer:
- When the body size of animals is large, the diffusion pressure alone cannot take care of oxygen delivery to all parts of the body.
- Instead haemoglobin of RBC take up oxygen from the air in the air into the lungs and carry it to tissues which are deficient in oxygen before releasing it.
Question 52.
Read the paragraph and answer the following questions.
It is necessary to move the food in a regulated manner along the digestive tube so that it can be processed properly in each part. The lining of canal has muscles that contract rhythmically in order to push the food forward. These peristaltic movements occur all along the gut.
1. What is the movement mentioned here ?
Answer:
Peristaltic movement.
2. What is the need of this movement ?
Answer:
Food digested and absorbed in different parts, so food must moved.
Question 53.
What is the role of blood in our body ?
Answer:
Blood being a fluid connective tissue. Blood consists of a fluid medium called plasma in which the cells are suspended. Plasma transports food, carbon dioxide and nitrogenous wastes in dissolved form. Oxygen is carried by the red blood corpuscles. Many other substances like salts, are also transported by the blood. We thus need a pumping organ to push blood around the body.
Question 54.
Why plants have slow transport system ?
Answer:
- Plants do not move, and plant bodies have a large proportion of dead cells in many tissues.
- As a result, plants have low energy needs, and can use relatively slow transport systems.
Question 55.
What is the transport system in plants ?
Answer:
- Plant transport systems will move energy stores from leaves and raw materials from roots.
- These two pathways are constructed as independently organized conducting tubes.
- One, the xylem moves water and minerals obtained from the soil.
- The other, phloem transports products of photosynthesis from the leaves where they are synthesized to other parts of the plant.
Question 56.
What is the main function of the circulatory system ?
Answer:
The main function of the circulatory system is to transport oxygen, nutrients, hormones, and waste products throughout the body, facilitating the exchange of substances between the cells and the external environment.
Question 57.
Explain the difference between arteries and veins.
Answer:
Arteries carry oxygenated blood away from the heart to the body tissues, while veins carry deoxygenated blood from the body tissues back to the heart. Arteries typically have thicker walls to withstand the pressure of blood pumped by the heart, while veins have valves to prevent the backflow of blood.
Question 58.
What is the role of red blood cells in the circulatory system ?
Answer:
Red blood cells, or erythrocytes are responsible for transporting oxygen from the lungs to the body tissues and carrying carbon dioxide, a waste product, from the tissues back to the lungs for exhalation.
Question 59.
Define the term "capillaries" in the context of the circulatory system.
Answer:
Capillaries are tiny, thin-walled blood vessels that connect arteries and veins. They are the site of nutrient and gas exchange between the blood and surrounding tissues. The thin walls of capillaries allow for the diffusion of substances such as oxygen, nutrients, and waste products.
Question 60.
What is the function of the heart in the circulatory system?
Answer:
The heart serves as the muscular pump that propels blood throughout the circulatory system. It contracts to pump oxygenated blood to the body and deoxygenated blood to the lungs for oxygenation.
Question 61.
How is blood transported to and from the heart?
Answer:
Blood is transported to the heart through two main veins: the superior and inferior vena cava. The superior vena cava carries deoxygenated blood from the upper body, while the inferior vena cava transports deoxygenated blood from the lower body.
Blood is pumped out of the heart through the pulmonary artery, carrying deoxygenated blood to the lungs for oxygenation. Oxygenated blood returns to the heart via the pulmonary veins, entering the left atrium. The heart then pumps oxygenated blood into the systemic circulation through the aorta.
Question 62.
Define Cardiac Cycle.
Answer:
The cardiac cycle refers to the sequence of events that occur during one complete heartbeat. It includes systole (contraction) and diastole (relaxation) phases of both the atria and ventricles. The contraction of the heart chambers leads to the ejection of blood, while relaxation allows the chambers to fill with blood. The cardiac cycle ensures the continuous and coordinated pumping of blood throughout the circulatory system.
Question 63.
Explain the process of water uptake in plants.
Answer:
Plants absorb water through their roots by a process called osmosis. The root hairs, present in the root system, increase the surface area for water absorption. As the soil water has a higher concentration of water compared to the root cells, water moves into the roots through osmosis. This water is then transported upwards through the xylem vessels to other parts of the plant.
Question 64.
What is transpiration, and how does it contribute to water movement in plants ?
Answer:
Transpiration is the process of water loss from the aerial parts of plants, primarily through small pores called stomata on the leaves. It occurs as water evaporates from the leaf surface Into the atmosphere. Transpiration creates a negative pressure in the leaf, known as suction or tension. This negative pressure pulls water from the roots, through the xylem vessels, to replace the water lost through transpiration. Thus, transpiration plays a crucial role in the upward movement of water in plants.
Question 65.
Differentiate between xylem and phloem tissues.
Answer:
Xylem and phloem are vascular tissues in plants with distinct functions. Xylem is responsible for the upward transport of water and minerals from the roots to other parts of the plant. It consists of vessels and tracheids. Phloem on the other hand, is involved in the bidirectional transport of nutrients, primarily sugars produced during photosynthesis, from the leaves to other plant tissues. Phloem comprises sieve tubes and companion cells. In summary, xylem transports water, while phloem transports nutrients in plants.
Question 66.
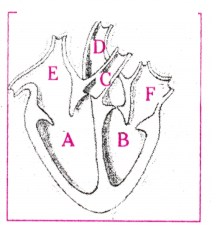
Identify any two parts from the above diagram which carry oxygenated and deoxygenated blood.
Answer:
Oxygenated blood: B - left vertricle, D - aorta, F - left auricle
Deoxygenated blood: A - right ventricle, C - Pulmonary artery, E - right auricle
Question 67.
Which chamber of the heart receives oxygen rich blood from lungs and how does it enters the Artery ?
Answer:
- The left atrium receives oxygen rich blood from the atrium it passes into left ventricle.
- When the left ventricle contracts, the oxygen rich blood is pumped into the artery for transportation to the cells.
Question 68.
How blood circulation occurs in fishes ?
Answer:
Fishes have 2-chambered heart. The blood is pumped to gills and is oxygenated there. Then it passes directly to the body. The blood goes only once through the heart during one cycle of passage through the body.
Question 69.
Birds and mammals, the left and right side of the heart are separated. Give reason.
Answer:
- The separation keeps oxygenated and deoxygenated blood from mixing, allowing a highly efficient supply of oxygen in the body.
- This is useful in animals that have high energy needs which constantly use energy to maintain their body temperature.
Question 70.
In human heart there is no mixing of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood. Give reason.
Answer:
- There is no mixing of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood due to presence of inter auricular and inter-ventricular septum.
- On the other hand valves are present in the heart which allows the movement of blood in one direction only.
Question 71.
What happens to the food once it enters our body ?
Answer:
The digestive system converts the foods we eat into their simplest forms, like sugars into glucose, proteins into amino acids and fats into fatty acids. The broken-down food is then absorbed into the bloodstream from the small intestine and the nutrients are carried to each cell in the body.
Question 72.
What happens if this system of tubes develops a leak ?
Answer:
Think about situations when we are injured and start bleeding. Naturally the loss of blood from the system has to be minimized. In addition, leakage would lead to a loss of pressure which would reduce the efficiency of the pumping system. To avoid this, the blood has platelet cells which circulate around the body and plug these leaks by helping to clot the blood at these points of injury.
Question 73.
Read the paragraph and answer the following questions.
Fishes, on the other hand, have only two chambers to their hearts and the blood is pumped to the gills, is oxygenated there and passes directly to the rest of the body. Thus, blood goes only once through the heart in the fish during one cycle of passage through the body. On the other hand, it goes through the heart twice during each cycle in other vertebrates. This is known as double circulation.
1. Which animals have double circulation ?
Answer: Vertebrates have double circulation.
2. How many heart chambers does a fish have ?
Answer: Fish have two chambers heart.
Question 74.
Define excretion.
Answer:
Excretion is the process of eliminating waste products and excess substances, such as urea and salts, from the body to maintain a proper balance of chemicals and prevent the buildup of harmful substances.
Question 75.
Name the nitrogenous waste product produced in humans and explain its formation.
Answer:
The nitrogenous waste product produced in humans is urea. It is formed in the liver through the breakdown of excess amino acids, a process known as deamination. The ammonia released during deamination is combined with carbon dioxide to produce urea, which is less toxic and more water-soluble, making it easier to be excreted.
Question 76.
What role do the nephrons play in excretion ?
Answer:
Nephrons are the functional units of the kidneys responsible for the process of filtration, reabsorption, and secretion. They filter blood, reabsorb essential substances, and excrete waste products, ultimately forming urine.
Question 77.
Explain the significance of the urinary system in maintaining homeostasis.
Answer:
The urinary system, consisting of the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra, plays a crucial role in maintaining homeostasis by regulating the balance of water, electrolytes, and other substances in the body. It helps eliminate metabolic waste products, control blood pressure, and maintain the proper concentration of ions in the blood.
Question 78.
Describe the process of urine formation in the kidneys.
Answer:
Urine formation in the kidneys involves three main processes: filtration, reabsorption,
and secretion. Blood is filtered in the glomerulus, and the filtrate undergoes reabsorption of essential substances (such as glucose and ions) in the renal tubules. Meanwhile, unwanted substances are secreted into the tubules. The final product, urine, is then transported to the bladder for storage and eventual elimination.
Question 79.
Explain the process of transpiration in plants in two sentences.
Answer:
Transpiration in plants is the loss of water vapor from the aerial parts, mainly through stomata on leaves. It occurs as a result of water movement from the roots to the leaves, where it evaporates into the atmosphere.
Question 80.
Name the specialized structures in plants responsible for the excretion of excess water and dissolved minerals.
Answer:
The specialized structures in plants responsible for the excretion of excess water and dissolved minerals are the stomata.
Question 81.
Describe the role of vacuoles in the excretion process of plant cells.
Answer:
Vacuoles in plant cells play a crucial role in excretion by storing and transporting waste products, such as excess salts and metabolic byproducts, helping to maintain cellular homeostasis.
Question 82.
How do plants eliminate metabolic wastes resulting from cellular processes ?
Answer:
Plants eliminate metabolic wastes through various processes, including the storage of waste products in vacuoles, shedding of leaves, and excretion through root cells into the soil.
Question 83.
State one environmental factor that influences the rate of transpiration in plants.
Answer:
One environmental factor that influences the rate of transpiration in plants is humidity. Higher humidity reduces the rate of transpiration, while lower humidity increases it.
Question 84.
What other function do you think is served by the gastric acid ?
Answer:
a) Gastric Acid makes the stomach’s habitat acidic.
b) It activates inactive pepsinogen into pepsin. Pepsin helps in protein digestion in the stomach.
c) It also kills bacteria that are brought into our bodies through food.
Question 85.
We have often heard adults complaining about ‘acidity’. Can this be related to gastric acid ?
Answer:
Yes, acidity is related to gastric juice. Acidity occurs when the gastric glands in the stomach produce an overabundance of acid and the kidneys can not get rid of it. It usually comes with heartburn, reflux, and indigestion. Typically, acidity is caused by consuming extra spicy food, coffee, overeating, having a low-fiber diet.
Question 86.
How is urine produced ?
Answer:
The purpose of making urine is to filter out waste products from the blood. Just as CO2 is removed from the blood in the lungs, nitrogenous waste such as urea or uric acid are removed from blood in the kidneys and formed urine.
Question 87.
What is the purpose of making urine in the human body ? Name the organs that stores and releases the urine.
Answer:
To filter out nitrogenous waste products like urea and uric acid from the blood in humans.
Organ for storage : Urinary Bladder; Organ for release; Urethra.
Question 88.
Name the substances other than water, that are reabsorbed during urine formation. What are the two parameters that decide the amount of water that is reabsorbed in the kidney ?
Answer:
Glucose, amino acids, salts, and a major amount of water are selectively re-absorbed as the urine flows along the tube. The amount of water reabsorbed depends on how much excess water there is in the body, and on how much of dissolved waste there is to be excreted.
Question 89.
List two major steps involved in the formation of urine and state in brief their functions.
Answer:
Filtration Nitrogenous wastes such as urea, uric acid are removed from the blood. Reabsorption : Glucose, amino acids, salts and major amount of water are selectively reabsorbed.
Question 90.
State three vital functions of the human kidneys.
Answer:
The three vital functions of human kidneys are
- Kidneys act as an excretory organ in human body to remove toxic wastes from the body.
- Kidneys also maintain the concentration of water and mineral ions in the body.
- It regulates blood pressure by controlling the fluid balance in the body.
Question 91.
Why plants coated with vaseline or wax do not remain healthy for a long time ? Give any two reasons.
Answer:
- Because they will not get oxygen for respiration.
- They will not get carbondioxide for photosynthesis.
Question 92.
More urine is produced in winter - Give Reason.
Answer:
- Due to the cold conditions, our body does not lose the water to form sweat.
- That remaining water is eliminated as urine.
- So more urine is produced in winter.
Important Questions on Life Processes Class 10 - 4 Marks
Question 1.
Why do we need food ?
Answer:
1. To maintain,the body life processes are needed to prevent damage and break¬down, energy1 is needed for them. This energy comes from outside the body of the individual organism. So there must be a process to transfer a source of energy from outside the body of the organism, which we call food.
If the body size of the organism is to grow, additional raw material will also be needed from outside. Since life on earth depends on carbon based molecules, most of these food sources are also carbon-based.
2. If the body size of the organisms is to grow, additional raw material will also be needed from outside. Since life on earth depends on carbon based molecules, most of these food sources are also carbon-based.
Question 2.
Why do we need oxygen ?
Answer:
Every organism’s body needs to grow. For this, a series of chemical reactions in the body are necessary. Oxidising-reducing reactions are some of the most common chemical means to break-down molecules. For this, many organisms use oxygen sourced from outside the body. The process of acquiring oxygen from outside the body, and to use it in the process of break-down of food sources for cellular needs, is what we call respiration.
Question 3.
Draw the neat labelled diagram of the cross section of a leaf.
Answer:
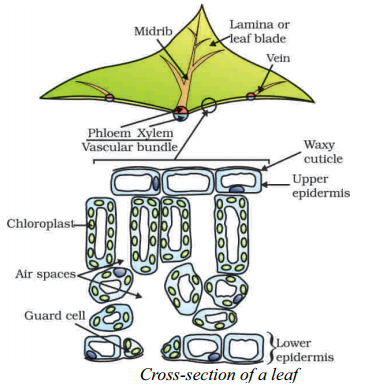
Question 4.
Draw the neat labelled diagram of stomata
(OR)
A student is observing the temporary mount of a leaf peel under a microscope. Draw labelled diagram of the structure of stomata as seen under the microscope.
Answer:

Question 5.
What are the stomata? How do they work?
Answer:
a) Stomata are tiny pores present on the surface of the leaves. Massive amounts of gaseous exchange takes place in the leaves through these pores for the purpose of photosyn?hesis.
b) Since large amounts of water can also be lost through these stomata, the plant closes these pores when it does not need carbon dioxide for photosynthesis.
c) The opening and closing of the pore is a function of the guard cells.
d) The guard cells swell when water flows into them, causing the stomatal pore to open. Similarly the pore closes if the guard cells shrink.
Question 6.
How do plants obtain their raw material to build their body?
Answer:
- Plants also need other raw materials for building their body.
- Water used in photosynthesis is taken up from the soil by the roots in terrestrial plants.
- Other materials like nitrogen, phosphorus, iron and magnesium are taken up from the soil.
- Nitrogen is an essential element used in the synthesis of proteins and other compounds. This is taken up in the form of inorganic nitrates or nitrites. Or it is taken up as organic compounds which have been prepared by bacteria from atmospheric nitrogen.
Question 7.
Explain the nutrition process in unicellulars like amoeba
Answer:
- Amoeba takes in food using temporary finger-like extensions of the cell surface which fuse over the food particle forming a food-vacuole.
- Inside the food vacuole, complex substances are broken down into simpler ones which then diffuse into the cytoplasm.
- The remaining undigested material is moved to the surface of the cell and thrown out.
- In Paramoecium, which is also a unicellular organism, the cell has a definite shape and food is taken in at a specific spot. Food is moved to this spot by the movement of cilia which cover the entire surface of the cell.

Question 8.
Explain the role of the stomach in digestion.
Answer:
- The muscular walls of the stomach help in mixing the food thoroughly with more digestive juices.
- The digestion in the stomach is taken care of by the gastric glands present in the wall of the stomach.
- These release hydrochloric acid, a protein digesting enzyme called pepsin, and mucus.
- The hydrochloric acid creates an acidic medium which facilitates the action of the enzyme pepsin.
- The mucus protects the inner lining of the stomach from the action of the acid under normal conditions.
Question 9.
Write about dental caries.
Answer:
- Dental caries or tooth decay causes gradual softening of enamel and dentine.
- It begins when bacteria acting on sugars produce acids that soften or demineralise the enamel.
- Masses of bacterial cells together with food particles stick to the teeth to form dental plaque.
- Saliva cannot reach the tooth surface to neutralize the acid as plaque covers the teeth.
- Brushing the teeth after eating removes the plaque before the bacteria produce acids.
- If untreated, microorganisms may invade the pulp, causing inflammation and infection.
Question 10.
Give the name of the enzyme present in the fluid in our mouth cavity. State the gland which produces it. What would happen to the digestion process if this gland stops secreting this enzyme ?
Answer:
- Salivary amylase is the enzyme present in the fluid of mouth cavity.
- It is produced by salivary glands.
- This enzyme breaks down starch which is a complex molecule to give simple sugar.
- The food is mixed thoroughly with saliva and moved around the mouth while chewing by the muscular tongue.
- Without amylase, we cannot digest carbohydrates and sugars in the mouth.
Question 11.
Differentiate between autotrophs and heterotrophs.
Answer:
| Autotrophs |
Heterotrophs |
| 1. The organisms which prepare their own food are called autotrophs. |
1. The organisms, which are not capable of synthesizing their own food and depend on other organisms for their nourishment are called heterotrophs. |
| 2. They include all green plants which are capable of performing photosynthesis. |
2. They include fungi and other non-green plants which may be parasites and saprophytes. They draw their nourishment plants which may be parasites and form living hosts or from dead and decaying organisms. |
Question 12.
How is the wall of small intestine adapted for performing the function of absorption of food ?
Answer:
Digested food is taken up by the walls of the intestine. The inner lining of the small intestine has numerous finger-like projections called villi which increase the surface area for absorption. The villi are richly supplied with blood vessels which take the absorbed food to each and every cell of the body, where it is utilised for obtaining energy, building up new tissues and the repair of old tissues.
Question 13.
Mention the differences between Pepsin and Trypsin.
Answer:
| Pepsin |
Trypsin |
| 1. It is released by the gastric glands in stomach. |
1. It is released by the pancreas. |
| 2. Pepsin requires hydrochloric acid which creates acidic medium for enzyme activity. |
2. Trypsin requires alkaline environment for its action, which is maintained by the bile juice. |
Question 14.
The Figure shown below represents an activity to prove the requirements for photosynthesis. During this activity, two healthy potted plants were kept in the dark for 72 hours. After 72 hours, KOH is kept in the watch glass in setup X and not in setup Y. Both these setup are air tight and have been kept in light for 6 hours. Then, iodine test is performed with one leaf from each of the two plants X and Y.
Answer:
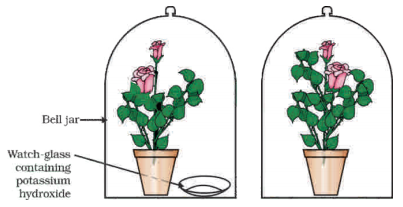
1. This experimental set up is used to prove essentiality of which of the following requirements of photosynthesis ?
Answer:
Carbondioxide
2. The function of KOH is to absorb
Answer:
Carbondioxide
3. Which of the following statements shows the correct results of Iodine Test performed on the leaf from plant X and Y respectively ?
Answer:
Blue - black colour would be obtained on the leaf of plant Y and no change in colour on leaf of plant X.
4. Write the steps can be followed for making the apparatus air tight ?
Answer:
- placing the plants on glass plate and
- applying aseline to seal the bottom of jar.
Question 15.
State the events occurring during the processes of photosynthesis.
Answer:
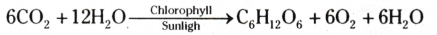
The following events occur during this process :
- Absorpotion of light energy by chlorophyll.
- Conversion of light energy to chemical energy.
- Splitting of water molecule into hydrogen and oxygen.
- Reduction of carbondioxide to carbohydrates.
Question 16.
Observe this diagram and answer the following questions.
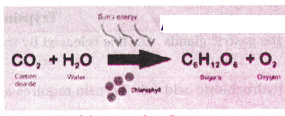
1. What are the reagents in this equation ?
Answer: CO2 and H2O.
2. Which type of reaction is it ?
Answer: Its anabolic and endothermic reaction.
3. Where is the energy for this equation ?
Answer: Solar energy.
4. What are the end products in this reaction ?
Answer: Starch and oxygen.
Question 17.
Draw the neat labelled diagram of the human digestive system.
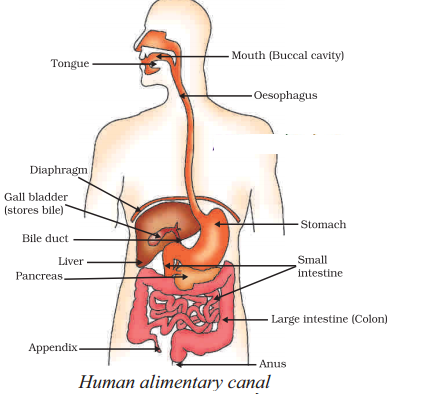
Answer:
Question 18.
Observe the diagram and answer the following questions.

1. What is the upper layer of the leaf ?
Answer: Waxy cuticle
2. What are the pores that are seen on the lower side of the leaf ?
Answer: Stomata.
3. What are the organelles that perform photosynthesis ?
Answer: Chloroplast.
4. What are the cells that surround the stomata ?
Answer: Guard cells.
Question 19.
Observe the diagram and answer the following questions.

1. What is the longest part in the alimentary canal?
Answer: Small intestine
2. Which connects the mouth to the stomach ?
Answer: Oesophagus
3. What is the biggest digestive gland ?
Answer: Liver
4. Where does the reabsorption take place ?
Answer: Large intestine
Question 20.
Why is photosynthesis important to humans ?
Answer:
- Photosynthesis is responsible for the oxygen that makes up the breathable air humans depend on.
- Photosynthesis is the process through which light energy (solar energy) is transformed into chemical energy.
- It is the basis for all life on earth.
- Humans depend on photosynthesis to make the food they consume, as a source of energy to produce heat, light and electricity, on a daily basis.
- Additionally, autotrophs are producers in almost all food chains, therefore this mechanism is essential for humans as well.
- Since oxygen, a necessary component for both animal and human survival, is released as a byproduct of photosynthesis, it is crucial for both people and animals.
Question 21.
What will help you to keep your digestive system healthy ?
Answer:
- Include fiber-rich food in your diet.
- Limit intakes of fatty foods.
- Chew your food properly.
- Incorporate probiotics in your diet.
- Water is essential for a smooth digestive system.
- Regular exercise make your digestion good.
Question 22.
What precautions should we take to keep your teeth healthy?
Answer:
- Take care of your teeth and mouth.
- Brush your teeth twice a day with fluoride toothpaste.
- Observe your teeth regularly.
- Visit your dentist routinely for a checkup and cleaning.
- Eat a well-balanced diet.
- Quit smoking. Smoking increases your risk for gum disease.
- Avoid sugar content food item like chocolates and cool drinks.
Question 23.
Write About ATP.
Answer:
ATP is the energy currency for most cellular processes. The energy released during the process of respiration is used to make an ATP molecule from ADP and inorganic phosphate.
Endothermic processes in the cell then use this ATP to drive the reactions. When the terminal phosphate linkage in ATP is broken using water, the energy equivalent to 30.5 kJ/mol is released.
Think of how a battery can provide energy for many different kinds of uses. It can be used to obtain mechanical energy, light energy, electrical energy and so on. Similarly, ATP can be used in the cells for the contraction of muscles, protein synthesis, conduction of nervous impulses and many other activities.
Question 24.
What are the types of respiration ?
Answer:
There are two types of respiration:
Aerobic respiration : It is a type of cellular respiration that takes place in the presence of oxygen to produce energy. It is a continuous process that takes place within the cells of animals and plants. This process can be explained with the help of the chemical equation:
Glucose(C2H12O6) + Oxygen(6O2) → Carbon dioxide(6CO2) + Water(6H2O)+ Energy (ATP)
Anaerobic respiration:
It is a type of cellular respiration that takes place in the absence of oxygen to produce energy. The chemical equation for anaerobic respiration is
Glucose(C6H12O6) → Alcohol 2(C2H5OH) + Carbon dioxide 2(CO2) + Energy (ATP )
Question 25.
How gaseous exchange takes place in pants ?
Answer:
- Plants exchange gases through stomata, and the large intercellular spaces ensure that all cells are in contact with air.
- Carbon dioxide and oxygen are exchanged by diffusion here. They can go into cells, or away from them and out into the air.
- The direction of diffusion depends upon the environmental conditions and the requirements of the plant.
- At night, when there is no photosynthesis occurring, CO2 elimination is the major exchange activity going on.
- During the day, CO2 generated during respiration is used up for photosynthesis, hence there is no CO2 release. Instead, oxygen release is the major event at this time.
Question 26.
What is the need of the respiratory system in organisms ?
Answer:
- Terrestrial organisms use the oxygen in the atmosphere for respiration. This oxygen is absorbed by different organs in different animals.
- All these organs have a structure that increases the surface area which is in contact with the oxygen-rich atmosphere.
- Since the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide has to take place across this surface, this surface is very fine and delicate. In order to protect this surface, it is usually placed within the body.
- So there have to be passages that will take air to this area. In addition, there is a mechanism for moving the air in and out of this area where the oxygen is absorbed.
Question 27.
Why to say ’no’ to tobacco ?
Answer:
Using tobacco directly or any product of tobacco in the form of cigar, cigarettes, bidis, hookah, gutkha, etc., is harmful. Use of tobacco most commonly affects the tongue, lungs, heart and liver. Smokeless tobacco is also a major risk factor for heart attacks, strokes, pulmonary diseases and several forms of cancers. There is a high incidence of oral cancer in India due to the chewing of tobacco in the form of gutkha. Stay healthy; just say NO to tobacco and its products
Question 28.
In the experimental set up on ‘CO2 is released during respiration,’ if one forgets to keep the vial with KOH in the conical flask, how will the result vary ? Give details.
Answer:
- Respiration in plants can be studied in moist germinating seeds that release carbon dioxide (CO2) during respiration.
- Potassium hydroxide absorbs carbon dioxide released by the seeds and a partial vacuum is created in the flask as a result.
- This causes the water level in the delivery tube to rise.
- As KOH breaks down, the oxygen needed for cellular respiration is released.
- It serves as a temporary energy source for the respiring organism.
- It binds with carbon dioxide to form a solid, preventing CO2 production from affecting gas volume.
- Its attraction for water will cause water to enter the respirometer.
Question 29.
Draw a diagram of human respiratory system and label the parts.
Answer:
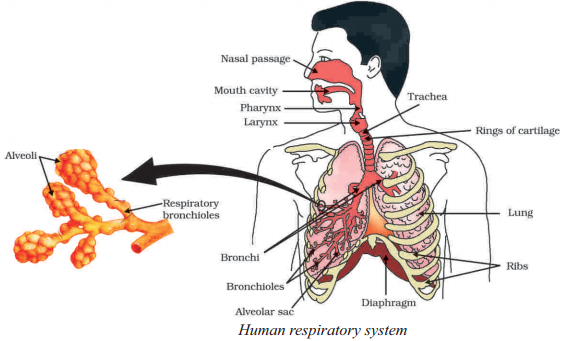
All living cells require energy for various activities. This energy is available by the breakdown of simple carbohydrates either using oxygen or without using oxygen.
- Energy in the case of higher plants and animals is obtained by ( )
A) Breathing
B) Tissue respiration
C) Organ respiration
D) Digestion of food
Answer:
A) Breathing
2. The graph below represents the blood lactic acid concentration of an athlete during a race of 400 m and shows a pek at point D.
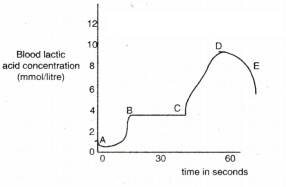
Lactic acid production has occurred in the athlete while running in the 400 m race. Which of the following processes explains this event ?
A) Aerobic respiration
B) Anaerobic respiration
C) Fermentation
D) Breathing
Answer:
B) Anaerobic respiration
Question 31.
How is breathing different from respiration ?
Answer:
| Breathing |
Respiration |
| 1. It is a mechanical process. |
1. It is a biochemical process. |
| 2. Atmospheric air is taken into the body and CO2 rich in air gives out of the body. |
2. Glucose is oxidised in the cells producing CO2 and water. |
| 3. Energy is not released in this process. |
3. Energy is released. |
| 4. It is the external respiration. |
4. It is the internal respiration. |
Question 32.
How do exchange of gases take place in aquatic animals ?
Answer:
Most of the aquatic animals like prawns, fish, tadpole larva use gills as respiratory organs. Respiration through gills is known as bronchial respiration.
Gills are richly filled with blood vessels. When water passes over the gills, oxygen dissolved in water is absorbed in the water and gives carbondioxide from the blood into the water. So, exchange of gases takes place through gills in the process of diffusion.
Question 33.
a) Write the reaction that occurs when glucose breakes down anaerobically in yeast.
b) Write the mechanism by which fishes breathe in water.
c) Name the balloon like structures present in lungs. List it’s two functions.
d) Name the respiratory pigment and write it’s role in human beings.
Answer:
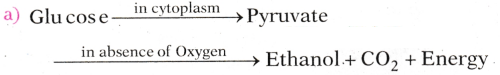
b) Fishes take in water through the mouth and force it past the gills where the dissolved oxygen is taken up by the blood.
c) Alveoli :
Functions : They contain network of blood vessels which exchange gases. They increase surface area of absorption of gases.
d) Haemoglobin :
Role : Due to high affinity for O2 it helps in it’s transport from alveoli to the tissues.
Question 34.
Read the flow chart and answer the following questions.
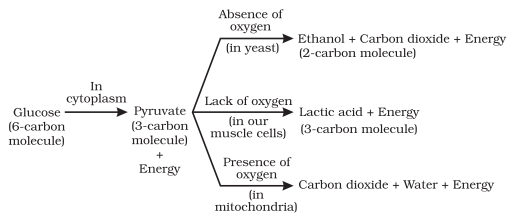
1. How many carbon molecules are present in glucose ?
Answer: Six Carbon Molecules.
2. How many pyruvates are formed from glucose ?
Answer: Two Pyruvates.
3. What are the end products of anaerobic respiration?
Answer: Ethanol, CO2
4. Where the glycolysis takes place ?
Answer: Cytoplasm.
Question 35.
What are 10 ways to keep your lungs healthy?
Answer:
These are things you can do to keep your lungs healthy :
- Stop smoking (and avoid secondhand smoke).
- Exercise regularly.
- Maintain a healthy diet and stay hydrated.
- Get annual check-ups.
- Stay up to date with vaccinations.
- Avoid outdoor air pollution exposure.
- Improve indoor air quality.
Question 36.
Draw the neat labelled diagram of the human heart.
Answer:
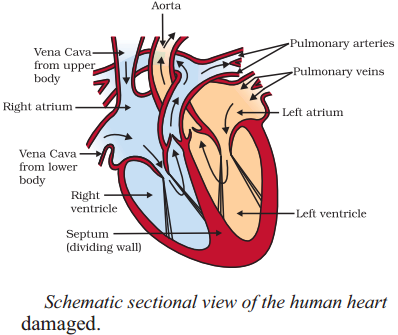
Question 37.
Draw the neat labelled diagram of the human double circulation heart.
Answer:
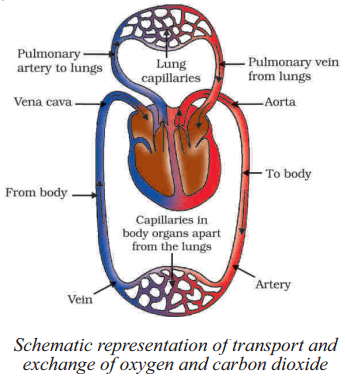
Question 38.
Why the right side of the blood separate from the left side ?
Answer:
- The separation of the right side and the left side of the heart is useful to keep oxygenated and deoxygenated blood from mixing.
- Such separation allows a highly efficient supply of oxygen to the body.
- This is useful in animals that have high energy needs, such as birds and mammals, which constantly use energy to maintain their body temperature.
Question 39.
Why in some animals heart pumps mixed blood ?
Answer:
- In animals like frogs and reptiles, the body temperature depends on the temperature in the environment.
- Such animals, like amphibians or many reptiles have three-chambered hearts, and tolerate some mixing of the oxygenated and deoxygenated blood streams.
Question 40.
What is a single circulatory heart ? And double circulation heart.
Answer:
Single Circulatory heart : Fishes, on the other hand, have only two chambers to their hearts, and the blood is pumped to the gills, is oxygenated there, and passes directly to the rest of the body. Thus, blood goes only once through the heart in the fish during one cycle of passage through the body, this is called a single circulatory heart.
Double circulatory heart: The blood goes through the heart twice during each cycle in other vertebrates. Like birds and mammals. This is known as double circulation.
Question 41.
Write about the lymph.
Answer:
- Lymph : There is another type of fluid also involved in transportation. This is called lymph or tissue fluid.
- Through the pores present in the walls of capillaries some amount of plasma, proteins and blood cells escape into intercellular spaces in the tissues to form the tissue fluid or lymph.
- It is similar to the plasma of blood but colorless and contains less protein.
- Lymph drains into lymphatic capillaries from the intercellular spaces, which join to form large lymph vessels that finally open into larger veins.
- Lymph carries digested and absorbed fat from intestine and drains excess fluid from extracellular space back into the blood.
Question 42.
Explain the water transport in plants.
Answer:
- In xylem tissue, vessels and tracheids of the roots, stems and leaves are interconnected to form a continuous system of water-conducting channels reaching all parts of the plant.
- At the roots, cells in contact with the soil actively take up ions. This creates a difference in the concentration of these ions between the root and the soil.
- Water, therefore moves into the root from the soil to eliminate this difference.
- This means that there is steady movement of water into root xylem, creating a column of water that is steadily pushed upwards.
Question 43.
What is the role of transpiration in transport of water ?
Answer:
- The loss of water in the form of vapour from the aerial parts of the plant is known as transpiration.
- Thus, transpiration helps in the absorption and upward movement of water and minerals dissolved in it from roots to the leaves. It also helps in temperature regulation.
- The effect of root pressure in transport of water is more important at night.
- During the day when the stomata are open, the transpiration pull becomes the major driving force in the movement of water in the xylem.
Question 44.
How are the food materials transported in plants?
Answer:
1. The products of metabolic processes, particularly photosynthesis, are moved from leaves, where they are formed, to other parts of the plant. This transport of soluble products of photosynthesis is called translocation.
2. It occurs in the part of the vascular tissue known as phloem. Besides the products of photosynthesis, the phloem transports amino acids and other substances.
3. These substances are especially delivered to the storage organs of roots, fruits and seeds and to growing organs.
4. The translocation of food and other substances takes place in the sieve tubes with the help of adjacent companion cells both in upward and downward directions.
Question 45.
How does translocation differ from transport of water ?
Answer:
- Unlike transport in xylem the translocation in phloem is achieved by utilizing energy.
- Material like sucrose is transferred into phloem tissue using energy from ATP.
- This increases the osmotic pressure of the tissue causing water to move into it.
- This pressure moves the material in the phloem to tissues which have less pressure. This allows the phloem to move material according to the plant’s needs.
- For example, in the spring, sugar stored in root or stem tissue would be transported to the buds which need energy to grow.
Question 46.
Explain the process of transport of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood in a human body.
Answer:
- In our heart blood enters twice and also pumped out twice from the heart.
- The deoxygenated blood from the body is brought to the right Atrium through vena- cava from where it is sent to right ventricle.
- From right ventricle, the blood is pumped to the lungs for oxygenation through pulmonary artery.
- The oxygenated blood from lungs again enters the left atrium of the heart through pulmonary veins.
- From left atrium it is send to left ventricle, from left atrium it is send to left ventricle, from where this oxygenated blood is pumped to different parts of the body through the arteries.
Question 47.
What are the materials transported by the following :
i) Xylem
ii) Pulmonary artery
iii) Pulmonary Vein
iv) Phloem
Answer:
i) Xylem : Transport water and minerals from roots to other parts of the plant.
ii) Pulmonary artery : Transport deoxygenated blood from heart to lungs.
iii) Pulmonary Vein : Transport oxygenated blood from lungs to heart.
iv) Phloem : Transport synthesised food from leaves to other parts of plant.
Question 48.
State the role and functions of (i) Blood and (ii) Lymph in human transport system.
Answer:
i. Blood: Blood is the fluid connective tissue that helps in transportation of various materials and gases.
Blood plasma transports digested food, different salts, carbon dioxide, hormones and nitrogenous wastes in dissolved form. Oxygen is carried by red blood cells.
ii. Lymph: Lymph is known as tissue fluid which consists of some amount of plasma, proteins and WBC’s. Lymph carries digested and absorbed fats from intestine and drains excess fluid from extracellular spaces into the blood.
Question 49.
Write the correct sequence of steps followed during journey of Oxygen rich blood from lungs to various organs of human body.
Answer:
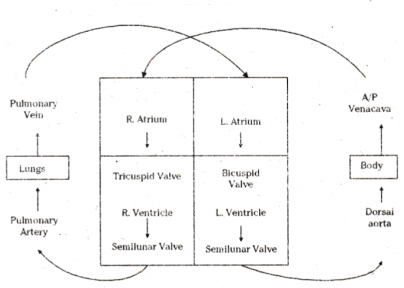
Question 50.
Why is transportation of water slow in plants as compared to animals ?
Answer:
- Plant bodies have a large proportion of dead tissues.
- So they have low energy needs, and can use relatively slow transport system.
- The distance over which transport system have to operate can be very large in plants such as very tall trees.
- Moreover plants do not have circulatory system and heart to pump the blood to supply water and food throughout the body.
- So, transportation of water and minerals is slow in plants as compared to animals.
Question 51.
Observe the diagram and answer the following questions.

1. How many chambers are there in the heart?
Answer: Four.
2. Which side of the heart has oxygenated blood?
Answer: Left.
3. Name the artery that carries oxygenated blood to the whole body.
Answer: Aorta.
4. Name the organ that receives deoxygenated blood and is converted into oxygenated?
Answer: Lungs.
Question 52.
Observe the diagram and answer the following questions.

1. Where the oxygenated blood converted into deoxygenated?
Answer: Body organs.
2. Which carries the blood to heart ?
Answer: Veins or Vena cava.
3. What is the circuit that occurs between heart and lungs ?
Answer: Pulmonary circuit.
4. What is the systemic cycle?
Answer: Circuit between heart and body organs.
Question 53.
Which steps do you follow for heart health ?
Answer:
To help heart health, you can :
- Eat healthy.
- Get active.
- Stay at a healthy weight.
- Quit smoking and stay away from secondhand smoke.
- Control your cholesterol and blood pressure.
- Avoid alcohol.
- Manage stress.
Question 54.
What precautions should be taken for high BP?
Answer:
Practice the following healthy living habits :
- Eat a healthy diet to help you avoid high blood pressure.
- Keep yourself at a healthy weight.
- Be physically active.
- Do not smoke.
- Avoid alcohol.
- Get enough sleep.
Question 55.
Explain the human excretory system.
Answer:
- The excretory system of human beings includes a pair of kidneys, a pair of ureters, a urinary bladder and a urethra.
- Kidneys are located in the abdomen, one on either side of the backbone.
- Urine produced in the kidneys passes through the ureters into the urinary bladder.
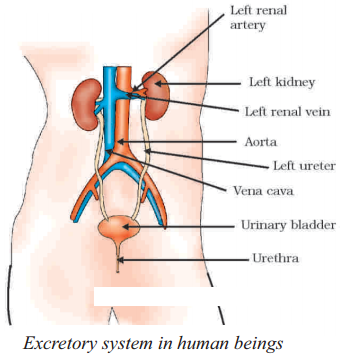
Question 56.
Draw the neat labelled diagram of nephron
Answer:
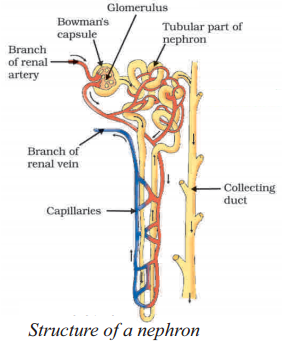
Question 57.
Write precautions for kidney health.
Answer:
"Gift Life, Donate Organs."
"Be an Organ Hero, Save Lives!"
"Donate Life, Give Hope."
"Organ Donation: Share the Gift of Life."
"Give the Ultimate Gift - Donate Organs."
"Be a Lifesaver, Be an Organ Donor."
"Join the Circle of Life - Donate Organs."
"Gift of Love, Gift of Life - Organ Donation."
Question 58.
The figure shown below represents a common type of dialysis called as Haemodialysis. It removes waste products from the blood. Such as excess salts, and urea which are insufficiently removed by the kidney in patients with kidney failure. During the procedure, the patient’s blood is cleaned by filtration through a series of semi-permeable membranes before being returned to the blood of the patient. On the basis of this, answer the following questions.
1. The hemodialyzer has semi-permeable lining of tubes which help
Answer: To pump purified blood back into the body of the patient.
2. Which one of the following is not a function of Artificial Kidney ?
Answer: To reabsorb essential nutrients from the blood.
3. The ‘used dialysing’ solution is rich in :
Answer: Urea and excess salts.
Question 59.
Mention the pathway of urine starting from the organ of it’s formation.
Name four substances which are reabsorbed from the initial filtration in the tubular part of the nephrons.
Answer:
Kidney → Ureters → Urinary bladder → Urethra.
The four substances re-absorbed from the initial filtrate are :
- Amino Acids
- Glucose
- Salts
- Major amount of water.
Question 60.
Observe the diagram and answer the following questions.
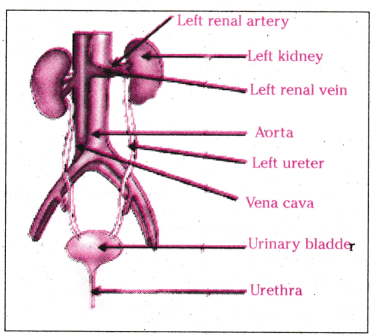
1. What is the main function of kidneys ?
Answer: Excretion
2. Where the urine is stored in the excretory system ?
Answer: Urinary bladder
3. Which connects the kidneys to the bladder ?
Answer: Ureter
4. What is the outlet of the urinary bladder ?
Answer: Urethra.
Question 61.
Observe the diagram and answer the following questions.
Answer:

1. What is the function of cup shaped structure in nephron ?
Answer: Blood filtration.
2. What are two major parts in nephron ?
Answer: Bowman’s capsule and Renal body.
3. Which factor influences the reabsorption ?
Answer: Mount of excess of water in the body.
4. Which collects the urine from nephrons ?
Answer: Collecting duct.
Question 62.
What should I do to keep my kidney healthy?
Answer:
For your kidney health
- Get tested for kidney disease.
- Monitor blood pressure.
- Manage blood sugar.
- Eat a balanced diet.
- Stay well hydrated.
- Stop smoking.
- Limit your medication use.
Question 63.
What are your suggestions to a dialysis patient ?
Answer:
- Take an active role in your treatment.
- Get adequate dialysis.
- Know and take your medications.
- Watch out for depression.
- Carry on with your life and exercise.
- Use time wisely while on treatment.
- Stick to your dialysis diet.
- Sleep well.
Question 64.
Write any four slogans to motivate people about organ donation.
Answer:
- Let’s share our life with others.
- Come ahead and take part in saving lives.
- No caste - no religion - save lives - donate organs.
- Giving a second change of life is in your hands.
Extra Questions on Life Processes Class 10 - 8 Marks
Question 1.
What are the types of heterotrophic nutrition ?
Answer:
Heterotrophic nutrition is a mode of nutrition in which organisms obtain nutrients by consuming other organisms or their products.
Heterotrophs cannot produce their own food through photosynthesis or chemosynthesis, so they rely on external sources for obtaining essential nutrients. There are three different types of heterotrophic nutrition :
Holozoic Nutrition : Involves the ingestion of whole or large pieces of food.
The ingested food is then broken down internally through processes like digestion. Examples include animals, including humans, that consume solid food and digest it internally.
Saprophytic Nutrition : Organisms feed on dead or decaying organic matter.
They absorb nutrients from the decomposed organic material.
Fungi and many bacteria exhibit saprophytic nutrition.
Parasitic Nutrition: Parasites obtain nutrients from a host organism.
They live on or inside the host and may harm the host in the process.
Examples include some worms, ticks, and certain plants.
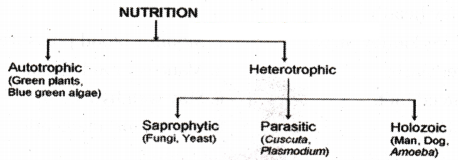
Question 2.
Write about the human digestive system.
Answer:
The human digestive system is a complex system responsible for the breakdown of food into nutrients that can be absorbed by the body. It consists of a series of organs and structures that work together to process food, those are:
Mouth : The process of digestion begins in the mouth. Teeth break down food into smaller pieces, and saliva, which contains enzymes, starts the chemical breakdown of carbohydrates.
Esophagus: The esophagus is a muscular tube that connects the mouth to the stomach. It transports the chewed and swallowed food (bolus) from the mouth to the stomach through a series of coordinated muscle contractions called peristalsis.
Stomach : The stomach serves as a storage organ and continues the digestion process. Gastric juices, including hydrochloric acid and enzymes, further break down food into a semi-liquid substance called chyme.
Small Intestine : Duodenum, Jejunum, Ileum: The small intestine is where most of the absorption of nutrients takes place. The chyme from the stomach mixes with bile (produced by the liver) and pancreatic juices (from the pancreas) to facilitate digestion and nutrient absorption.
Liver : The liver produces bile, which is stored in the gallbladder. Bile aids in the digestion and absorption of fats in the small intestine.
Gallbladder : The gallbladder stores and releases bile into the small intestine when needed to help with the digestion of fats.
Pancreas: The pancreas secretes digestive enzymes into the small intestine to further break down carbohydrates, fats, and proteins. It also produces insulin and glucagon, which are involved in regulating blood sugar levels.
Large Intestine (Colon) : The remaining undigested food, water, and electrolytes move into the large intestine, where water is absorbed, and the remaining material forms faeces. The colon also houses a complex microbial ecosystem that plays a role in the fermentation of undigested carbohydrates and the production of certain vitamins.
Rectum : The rectum stores faeces until it is ready to be eliminated.
Anus: The anus is the opening through which faeces are expelled from the body during the process of defecation.

Question 3.
Explain the digestion process in the small intestine.
Answer:
1. The small intestine is the site of the complete digestion of carbohydrates, proteins and fats.
2. It receives the secretions of the liver and pancreas for this purpose.
3. The food coming from the stomach is acidic and has to be made alkaline for the pancreatic enzymes to act.
4. Bile juice from the liver accomplishes this in addition to acting on fats.
5. Fats are present in the intestine in the form of large globules which makes it difficult for enzymes to act on them.
6. Bile salts break them down into smaller globules increasing the efficiency of enzyme action. This is similar to the emulsifying action of soaps on dirt.
7. The pancreas secretes pancreatic juice which contains enzymes like trypsin for digesting proteins and lipase for breaking down emulsified fats.
8. The walls of the small intestine contain glands which secrete intestinal juice.
9. The enzymes present in it finally convert the proteins to amino acids, complex carbohydrates into glucose and fats into fatty acids and glycerol.
Question 4.
List the steps of preparation of temporary mount of a leaf peel to observe stomata.
Answer:
- Pick a healthy leaf from the potted plant.
- Fold the leaf to gently pull the peel apart to separate a peeled section from the lower surface of the leaf. Use the forceps to perform this step. Allow the peel to remain in a watch glass holding water for some time.
- In the watch glass, stain the sample by adding some drops of safranin through a dropper.
- fake the peel out after 2-3 minutes. Set it on a clear glass slide.
- Add a drop of glycerin on the peel. Put a clear coverslip over it gently using a needle.
- Excess glycerin and stain can be removed using blotting paper.
- Examine the slide first under a low-power and then under a high-power magnification of a compound microscope.
Question 5.
a) A gas is released during photosynthesis. Name the gas and also state the way by which the gas is evolved ?
b) What are stomata ? What governs the opening and closing of stomata ?
Answer:
a)
- The gas released during the process of photosynthesis is oxygen. Oxygen is liberated which comes from the splitting of water molecule.
- During photosynthesis plants absorb carbondioxide and sunlight to produce carbohydrates.
- The solar energy trapped by chlorophyll breakes down water molecules by the process of photolysis. Photolysis of water releases oxygen.
b)
- Stomata are tiny pores present on the surface of the leaves.
- The opening and closing of stomatal pores are controlled by the turgidity of guard cells.
- When guard cells up take water from surrounding cells, swell to become swell to turgid body. This enlarges the pores in between and cause stornatal opening.
- When water is released they become flated.
- This closes the pores in between causing stornatal closing.
Question 6.
Explain the process of nutrition in Amoeba with the help of a diagram.
Answer:
The process of nutrition in amoeba involves in 5 steps :
- Ingestion
- Digestion
- Absorption
- Assimilation
- Egestion
Amoeba obtains food by phagocytosis a type of holozoic nutrition.
- Ingestion : Amoeba engulfs it’s food by using pseudopodia, which are temporary extensions of the cell surface. These pseudopodia fuse over the food particle forming a food vacuole.
- Digestion : Inside the food vacuole, complex substances of the food are broken down into simple ones.
- Absorption : The digested simple substances diffuses from food vacuole into cytoplasm.
- Assimilation : The digested food is utilised for metabolic activities.
- Egestion : The remaining undigested material is moved near the surface of the unicellular body of Amoeba and thrown outside.
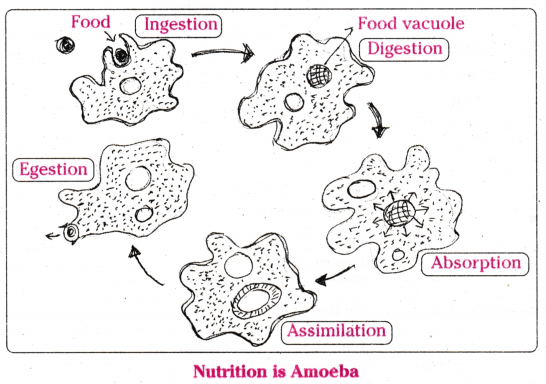
Question 7.
Explain the process of digestion with the help of a flow chart.
Answer:
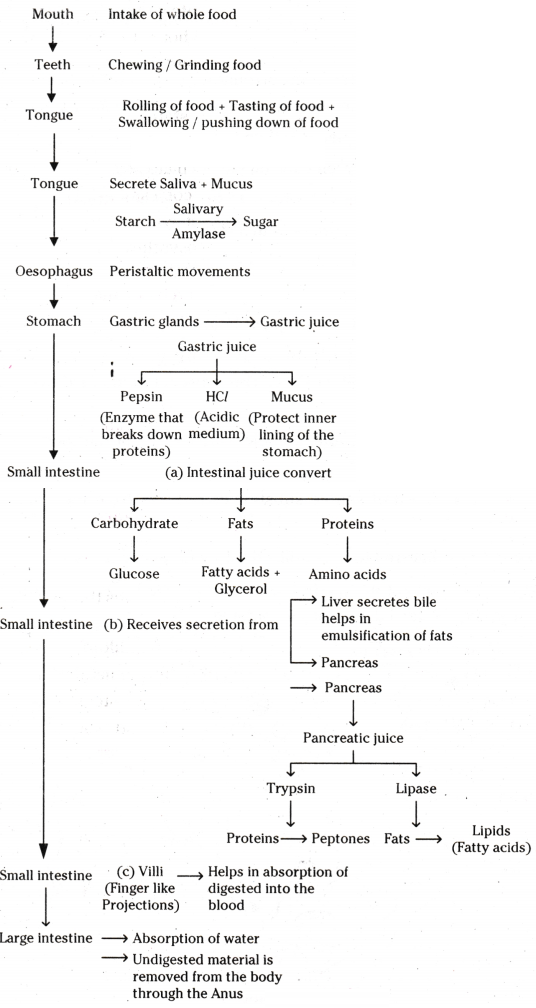
Question 8.
Explain an experiment to prove that sunlight is essential for photosynthesis.
Answer:
Experiment to prove that sunlight is essential for photosynthesis :
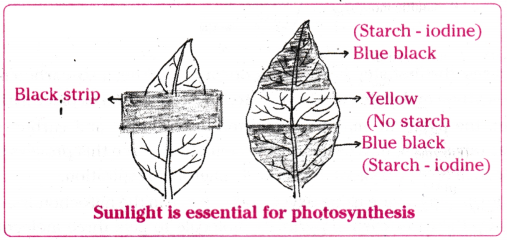
- Take a potted plant and keep it in dark for about 36 hours to destarch the leaves.
- Cover a part of a leaf with black strips on both the surfaces.
- Now place the leaf in sunlight for 6 hours.
- Pluck the leaf, remove the strip and test the leaf for starch using iodine solution.
- Boil the leaf in alcohol on the water-bath and dip it in iodine, solution.
- After applying iodine, the part which was covered by black strip remain colour- less.
- The part of the leaf which is exposed to sunlight becomes blue-black.
- This shows that the part which was exposed to light synthesized food.
- Hence we conclude that light is necessary for photosynthesis.
Question 9.
Explain the structure of stomata with a neatly labelled diagram.
Answer:
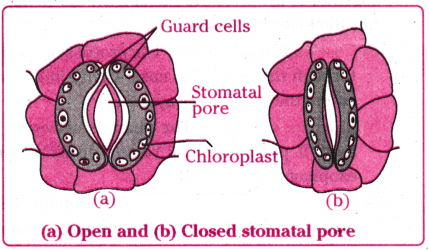
- Each stoma is a minute pore surrounded by two guard cells.
- They are present on the surface of the leaves.
- Massive amount of gaseous exchange takes place in the leaves through these pores for the purpose of photosynthesis.
- The guard cells are kidney shaped and contain numerous chloroplasts.
- The guard cells regulates the opening and closing of the stomatal pore.
- The guard cells swell when water flows into them causing the stomatal pore to open.
- The inflow of water in guard cells cause the stretching and bulging of outer thin walls in convex shape.
- This drags thick walls apart leading to opening the pore.
- When there is outflow of water from guard cells, the outer thin walls come to their original position resulting in closure of stomatal pore.
Question 10.
Write about the glucose breakdown process in the respiration.
Answer:
a) Break-down of glucose is the primary process in respiration.
b) Glucose breakdown completely into carbon dioxide and water.
c) Some organisms use other pathways that do not involve oxygen.
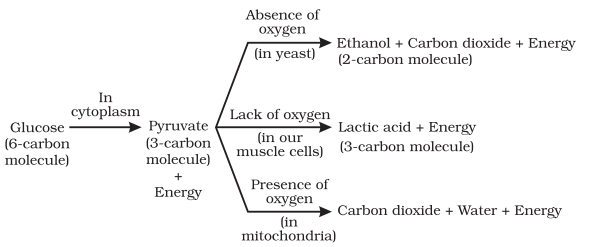
d) In all cases, the first step is the break-down of glucose, a six-carbon molecule, into a three-carbon molecule called pyruvate. This process takes place in the cytoplasm.
e) Further, the pyruvate may be converted into ethanol and carbon dioxide. This process takes place in yeast during fermentation. Since this process takes place in the absence of air (oxygen), it is called anaerobic respiration.
f) Breakdown of pyruvate using oxygen takes place in the mitochondria. This process breaks up the three-carbon pyruvate molecule to give three molecules of carbon dioxide. The other product is water. Since this process takes place in the presence of air (oxygen), it is called aerobic respiration.
g) The release of energy in this aerobic process is a lot greater than in the anaerobic process. Sometimes, when there is a lack of oxygen in our muscle cells, another pathway for the break-down of pyruvate is taken.
h) Here the pyruvate is converted into lactic acid which is also a three-carbon molecule. This build-up of lactic acid in our muscles during sudden activity causes cramps.
Question 11.
Describe the respiratory system in human beings.
Answer:
The human respiratory system is a complex network of organs and tissues that work together to facilitate the exchange of gases between the body and the environment. It has the following parts.

a) Nose and Nasal Cavity: The process of respiration begins with the inhalation of air through the nose. The nasal cavity filters, warms, and moistens the air before it enters the respiratory system.
b) Pharynx (Throat) : The pharynx serves as a common pathway for both air and food. It plays a crucial role in directing air into the trachea and food into the esophagus.
c) Larynx (Voice Box) : The larynx contains the vocal cords and is involved in speech production. It also acts as a passageway for air moving from the pharynx to the trachea.
d) Trachea (Windpipe) The trachea is a tube composed of cartilage rings that carries air from the larynx to the lungs. It is lined with ciliated cells and mucus-producing cells, which help trap and remove particles and microorganisms.
e) Bronchi and Bronchioles : The trachea divides into two bronchi, each leading to one lung. Inside the lungs, the bronchi further divide into smaller bronchioles. These structures carry air deeper into the lungs.
f) Alveoli : At the end of the bronchioles are tiny air sacs called alveoli. These sacs are surrounded by capillaries and are the site of gas exchange. Oxygen from the air diffuses into the bloodstream, while carbon dioxide moves from the blood into the alveoli to be exhaled.
Question 12.
Differenciate between Respiration and Combustion.
Answer:
| Respiration |
Combustion |
| 1. Respiration is a biological process occurs in living cells. |
1. Combustion is a non-biological process hence it is a non-cellular. |
| 2. It is a biophysical process. |
2. It is a physio - chemical process. |
| 3. It is the slow oxidation of glucose, which results in stepwise release of energy. |
3. It is a rapid oxidation of substance like coal and results in the release of the energy. |
| 4. Less than 50% energy is liberated as heat. |
4. Most of the energy is liberated as heat. |
| 5. Light is liberated in rare cases. |
5. Light and sound is liberated during combustion. |
| 6. Most of the energy trapped in ATP molecule. |
6. ATP is not formed. |
| 7. Respiration reactions are catalysed by enzymes. |
7. Enzymes are not involved in combustion. |
Question 13.
Explain with the help of a flow chart the path way of air in humans.
Answer:
Path way of air :
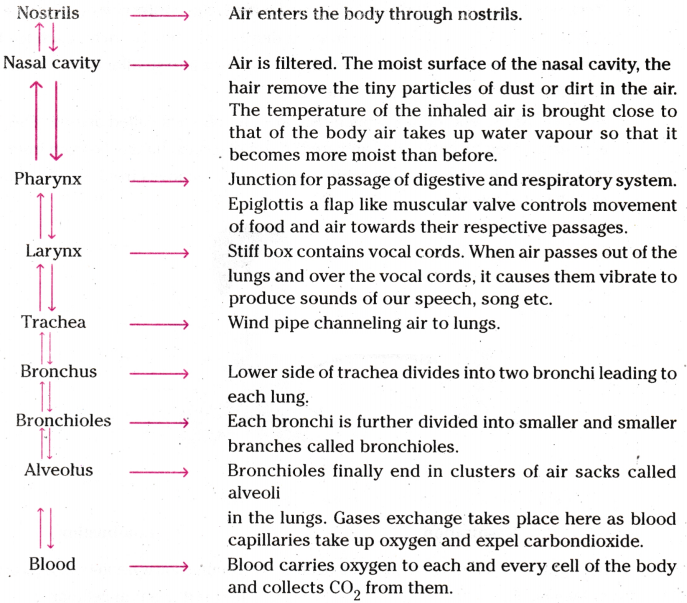
Question 14.
How the heart pumps blood?
Answer:
1. The heart is a muscular organ which is as big as our fist. Because both oxygen and carbon dioxide have to be transported by the blood.

2. The heart has different chambers to prevent the oxygen-rich blood from mixing with the blood containing carbon dioxide.
3. The carbon dioxide-rich blood has to reach the lungs for the carbon dioxide to be removed.
4. The oxygenated blood from the lungs has to be brought back to the heart. This oxygen-rich blood is then pumped to the rest of the body.
5. Oxygen-rich blood from the lungs comes to the thin-walled upper chamber of the heart on the left, the left atrium. The left atrium relaxes when it is collecting this blood.
6. It then contracts, while the next chamber, the left ventricle, relaxes, so that the blood is transferred to it.
7. When the muscular left ventricle contracts in its turn, the blood is pumped out to the body.
8. De-oxygenated blood comes from the body to the upper chamber on the right, the right atrium, as it relaxes.
9. As the right atrium contracts, the corresponding lower chamber, the right ventricle, dilates.
10. This transfers blood to the right ventricle, which in turn pumps it to the lungs for oxygenation. Since ventricles have to pump blood into various organs, they have thicker muscular walls than the atria do.
11. Valves ensure that blood does not flow backwards when the atria or ventricles contract.
Question 15.
What are the types in blood vessels ?
Answer:
Blood vessels are a crucial component of the circulatory system, responsible for transporting blood throughout the body. There are three main types of blood vessels:
1. Arteries: Arteries carry oxygenated blood (except for the pulmonary artery, which carries deoxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs). They have thick and elastic walls that allow them to withstand the high pressure generated by the heart’s pumping action. Arteries branch into smaller vessels known as arterioles.
2. Veins : Veins carry deoxygenated blood (except for the pulmonary veins, which carry oxygenated blood from the lungs to the heart). Veins have thinner walls compared to arteries and are less elastic. Valves are present in many veins to prevent the backflow of blood and assist in the return of blood to the heart. Veins merge into larger vessels called venules.
3. Capillaries: Capillaries are tiny, thin-walled vessels that connect arteries and veins. They facilitate the exchange of oxygen, nutrients, and waste products between the blood and surrounding tissues. Capillary walls are so thin that substances like oxygen and nutrients can pass through them to nourish the cells, while waste products can pass from the cells into the blood.
Question 16.
How the water transport in the plants ?
Answer:
Water transport in plants occurs through a specialized tissue called xylem. Xylem is responsible for the upward movement of water from the roots to the leaves and other parts of the plant. The process of water transport in plants have following.
Root Absorption : Water is absorbed from the soil by the roots through a process called osmosis. Root hairs, tiny extensions of root cells, increase the surface area for water absorption. The root cells actively transport minerals and water into the plants vascular system.
Root Pressure : In some plants, root pressure can contribute to water movement. This pressure is generated by active transport of ions into the root xylem, creating a pressure gradient that forces water upward.
Cohesion and Adhesion : These are two key concepts that facilitate water transport in plants. Cohesion refers to the tendency of water molecules to stick together, and adhesion refers to the attraction between water molecules and other substances. Together, these properties allow water to form a continuous column in the xylem vessels.
Capillary Action : Capillary action, facilitated by the narrow tubes of the xylem, helps in the upward movement of water against gravity. The cohesion between water molecules and the adhesion of water to the xylem vessel walls aid in this process. Transpiration : Transpiration is the process by which water vapor exits the.plant through small pores called stomata, mainly found on the leaves. As water evaporates from the stomata, it creates a pressure in the leaf, pulling water from the xylem vessels.

Question 17.
How is lymph an important fluid involved in transportation ? If lymphatic vessels get blocked, how would it affect the human body ? Elaborate.
Answer:
Lymphatic system :
- It is a subsystem of the vertebrate circulatory system that consists of a complicated network of arteries, tissues, and organs.
- It acts as a filter for microorganisms, organic wastes, poisons, and other debris.
- It transports lymphocytes throughout the body to combat infections.
- It maintains fluid homeostasis which is the fluid balance between the blood and tissues.
- Forms an important component of the body’s immune system and aids in the defense against germs and other intruders.
- In the digestive tract, it aids in the absorption of lipids and fat-soluble nutrients.
Lymphatic system failure causes :
- Fluid accumulated can cause edema and the body to swell up, destroying tissues and resulting in tissue death.
- Dead, disintegrating cells, dangerous bacteria, and viruses start accumulating in the body.
- Symptoms of a blocked lymphatic system include swelling, fatigue, bloating, depression, and excessive weight gain.
Question 18.
Explain the process of double circulation with the help of a flow chart.
Answer:
Double circulation :
- In our heart blood enters twice and also pumped out twice from the heart.
- The deoxygenated blood from the body is brought to the right Atrium through vena- cava from where it is sent to right ventricle.
- From right ventricle, the blood is pumped to the lungs for oxygenation through pulmonary artery.
- The oxygenated blood from lungs again enters the left atrium of the heart through pulmonary veins.
- From left atrium it is send to left ventricle, from left atrium it is send to left ventricle, from where this oxygenated blood is pumped to different parts of the body through the arteries.
- In this way the blood flows through the heart twice, that’s why it is called double circulation.

Question 19.
Describe and explain the variation in blood pressure throughout an individuals circulatory system during a single heartbeat.
Answer:
Blood pressure :
- The force that blood exerts against the wall of a vessel is called blood pressure.
- This pressure is much greater in arteries than in veins.
- Blood pressure is measured with an instrument called sphygmomanometer.
- The pressure of blood inside the artery during ventricular systole (contraction) is called systolic pressure. It occurs when the left ventricle contracts, pumping blood into arteries to be carried throughout the body.
- The pressure in artery during ventricular diastole (relaxation) is called diastolic pressure. Blood pumped from the right ventricle goes to the lungs.
- The normal systolic pressure is about 120 mm of Hg and diastolic pressure is 80 mm of Hg.
- High blood pressure is also called hypertension and is caused by the constriction of arterioles, which results in increased resistance to blood flow.
Question 20.
Mention the differences between blood and lymiph.
Answer:
| Blood |
Lymph |
| 1. Blood is red due to the presence of hemoglobins in the red blood cells. |
1. Lymph is colourless due to the absence of haemoglobin. |
| 2. Blood flows in blood vessels but does not contact with body tissues. |
2. The lymph bathes the body tissues. |
| 3. Blood flows from heart to body organs and returns to heart. |
3. The lymph flows from the tissues to the heart. |
| 4. Blood contains RBC, WBC, platelets and plasma. |
4. Lymph contains some amount of plasma and white blood cells. |
Question 21.
Write about the artificial kidney.
Answer:
Kidneys are vital organs for survival. Several factors like infections, injury or restricted blood flow to kidneys reduce the activity of kidneys. This leads to accumulation of poisonous wastes in the body, which can even lead to death. In case of kidney failure, an artificial kidney can be used. An artificial kidney is a device to remove nitrogenous waste products from the blood through dialysis.
Artificial kidneys contain a number of tubes with a semipermeable lining, suspended in a tank filled with dialysing fluid. This fluid has the same osmotic pressure as blood, except that it is devoid of nitrogenous wastes. The patient’s blood is passed through these tubes. During this passage, the waste products from the blood pass into dialysing fluid by diffusion.
The purified blood is pumped back into the patient. This is similar to the function of the kidney, but it is different since there is no reabsorption involved. Normally, in a healthy adult, the initial filtrate in the kidneys is about 180L daily. However, the volume actually excreted is only a litre or two a day, because the remaining filtrate is reabsorbed in the kidney tubules.
Question 22.
Write about organ donation.
Answer:
Organ donation is a generous act of donating an organ to a person who suffers from non-function of organ(s). Donation of an organ may be done by the consent of the donor and his/her family. Anyone regardless of age or gender can become an organ and tissue donor. Organ transplants can save or transform the life of a person.
Transplantation is required because recipient’s organ has been damaged or has failed by disease or injury. In organ transplantation the organ is surgically removed from one person (organ donor) and transplanted to another person (the recipient).
Common transplantations include corneas, kidneys, heart, liver, pancreas, lungs, intestines and bone marrow. Most organ and tissue donations occur just after the donor has died or when the doctor declares a person brain dead. But some organs such as kidney, part of a liver, lung, etc., and tissues can be donated while the donor is alive.
Question 23.
How plants excrete their waste materials ?
Answer:
- Plants use completely different strategies for excretion than those of animals.
- Oxygen itself can be thought of as a waste product generated during photosynthesis but it is reused in the respiration process.
- Like that CO2 is waste material in respiration that is used in photosynthesis.
- They can get rid of excess water by transpiration.
- For other wastes, plants use the fact that many of their tissues consist of dead cells, and that they can even lose some parts such as leaves.
- Many plant Waste products are stored in cellular vacuoles. Waste products may be stored in leaves that fall off.
- Other waste products are stored as resins and gums, especially in old xylem.
- Plants also excrete some waste substances into the soil around them.
Question 24.
Describe in brief how urine is produced in human body. ,
Answer:
Formation of urine involves four stages :
1. Glomerular filtration
2. Tubular reabsorption
3. Tubular secretion
4. Concentration of urine.
1. Glomerular filtration:
- Blood flows from renal artery to glomerulus through afferent arteriole.
- Filtration of blood occurs in glomerulus.
- Glomerular filtrate is also known as primary urine which almost equal to blood in chemical composition except the presence of blood cells.
2. Tubular reabsorption:
- The primary urine passes into proximal convoluted tubule.
- Useful substances like glucose, amino acids, sodium chloride, potassium ion, bicarbonate ion, water are reabsorbed into peritubular network.
3. Tubular secretion
- After reabsorption in proximal convoluted tubule, the urine travels through the loop of Henle into distal convoluted tubule.
- Here some other wastes like extra salts ions of K+, Na+, Cl+ and H+ secrete from peritubular capillaries into distal convoluted tubule which are surrounded by peritubular network.
4. Concentration of urine :
- 75% of water content of the nephric filtrate is reabsorbed in the region of proximal convoluted tubule and 10% of water passes out of filtrate through the osmosis in the area of loop of Henle.
- Concentration of urine takes place in the area of collecting tubes in the presence of hormone called vasopressin. The hormone is secreted only when concentrated urine is to be passed out.
Question 25.
How do leaves of plants helps in excretion ? Explain briefly.
Answer:
Leaves of plants helps in excretion in many ways :
- Excess of water in plants is removed by the process of transpiration and guttation.
- Carbondioxide and oxygen that can be considered as waste products of respiration and photosynthesis respectively are excreted out through stomata present on leaves.
- Leaves help in excretion through a process called abscission that is falling yellow leaves, to get rid of toxins etc.
- Waste products may be stored in leaves, bark and fruits. When these dead leaves, bark and ripen fruits fall off from the tree to get rid off these waste products.
- Some of the plants wastes get stored in the fruits in the solid bodies called Raphides Ex: Yam.
- The plants get rid off wastes by secreting them in the form of gums and resins.
- Plant roots also excrete some wastes into the soil.
Question 26.
What is artificial kidney ? How does it work ?
Answer:
- Artificial kidney consists of a number of tubes with semipermeable lining. (Selectively permeable membrane).
- These tubes are suspended in the tank filled with dialyzing fluid.
- The dialyzing fluid has the same concentration as blood plasma but it does not contain nitrogenous wastes.

Working :
- The blood of the patient is passed through dialyzing tubes.
- As blood passes through the tubes, the waste products like urea, ammonia etc. from the blood pass into dialysing fluid by diffusion.
- The purified blood is pumped back into the patient.
- Artificial kidney does filtration but no reabsorption as it is done by kidney.
- Dialysis containing nitrogen waste is changed from time to time.
- Normally, in a healthy adult, the initial filtrate in the kidney is about 180 litres dialy. But the volume actually excreted is only a litre or two a day, because the remaining filtrate is reabsorbed in the kidney tubules.
Question 27.
What are the differences between arteries and veins?
Answer:
| Arteries |
Veins |
| 1) Carry oxygenated blood from the heart. |
1) Carry deoxygenated blood to the heart. |
| 2) They have thicker walls. |
2) They have thinner walls. |
| 3) Tunica media is the thickest layer. |
3) Tunica adventitia is the thickest layer. |
| 4) These generally do not have valves. |
4) They have valves. |
| 5) Pulmonary artery carries deoxy- genated blood from the heart to the lungs. |
5) Pulmonary veins carry oxygenated blood from lungs to the heart. |
| 6) Their walls have higher elastin content. |
6) Their walls have less or no elastin content. |
| 7) The blood flowing is under high pressure. |
7) Blood flowing in veins have less pressure. |
| 8) Carbon dioxide levels in the blood are low. |
8) Carbon dioxide levels in the blood are high. |
| 9) Blood flowing through arteries is bright red in colour. |
9) Blood flowing through arteries is dark red in color. |